Fig. 5.
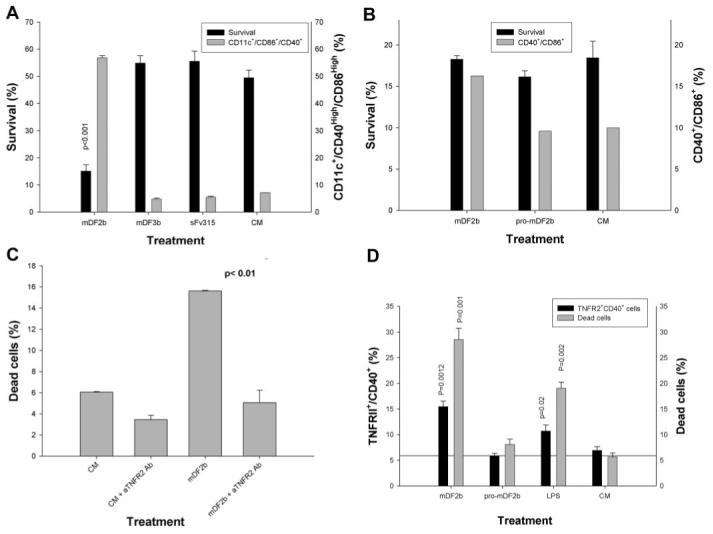
The mDF2β-induced cell death is mediated through TNF-α and its receptor TNFR2 but not TNFR1. BMDCs from nonfunctional TNFR1 (A) or TNFR1 and TNFR2 mice (B) were treated with mDF2β, mDF3β, and sFv315 or mock-treated for 3 days to assess cell survival (solid bars, left y-axis) or DC maturation (shaded bars, right y-axis), as described in Figure 3. (C) The mDF2β-induced death of B6/129 macrophage cells is abrogated in the presence of anti-mouse TNFR2-neutralizing mAb (10 μg/ml) but not isotype-matched IgG (10 μg/ml). The y-axis is in arbitrary proportion of Annexin V/PI-positive cells (dead cells). (D) TNFR2 is up-regulated on the surface of immortalized B6/129 macrophages treated overnight with mDF2β or LPS but not with mproDF2β. The cells were stained for TNFR2 and CD40 (solid bars, left y-axis) and Annexin/PI (shaded bars, right y-axis). All results shown (A-D) were reproduced at least two times, and the mean of the representative triplicate experiment is shown ± sem. P values are for comparisons of viability of cells treated with mDF2β and control protein sFv315 (A) or mproDF2β (D); between two groups as depicted by horizontal lines (C); or between mDF2β or LPS with mproDF2β (D). (B) The survival difference between mDF2β- and mproDF2β-treated groups was not insignificant.
