Figure 5.
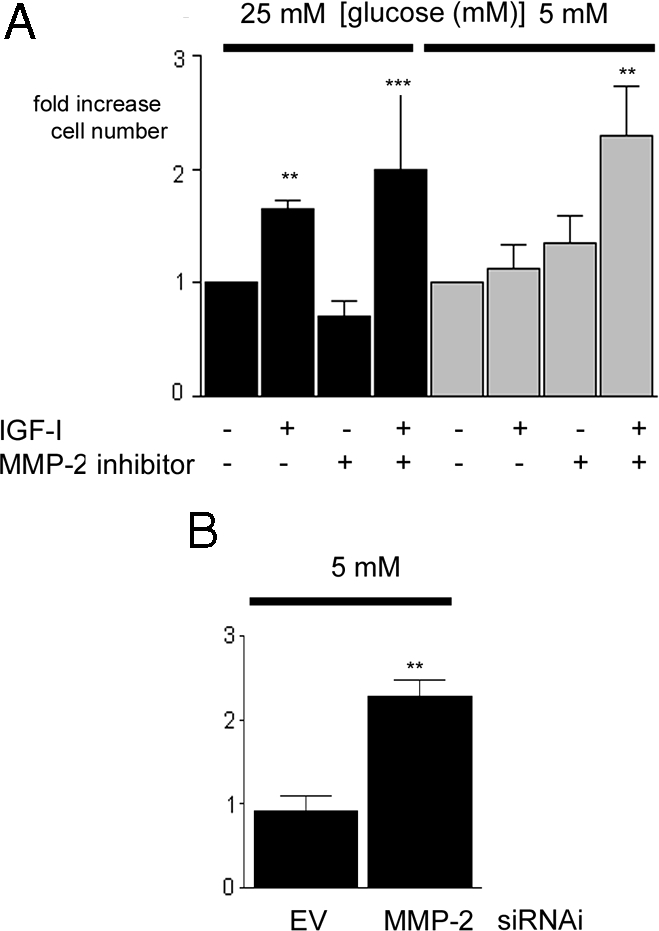
Inhibition of MMP-2 Protease Activity Enhances the Proliferative Response of SMC Maintained in 5 mm Glucose to IGF-I
A, Cells that had been grown in either 25 or 5 mm glucose were plated (2 × 104 cells per well) in 24-well plates for 24 h to allow attachment. After an overnight incubation in SFM, they were then exposed to IGF-I (50 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of the MMP-2 inhibitor (or vehicle control) with 0.2% platelet-poor plasma. After an additional 48 h, cell number was determined by trypan blue staining and counting. ***, P < 0.005 when cell number in response to IGF-I in cells grown in 5 mm glucose in the presence of the MMP-2 inhibitor is compared with the response of cells grown in 5 mm glucose alone; **, P < 0.01 when the response of SMC grown in 25 mm glucose with IGF-I is compared with SMC grown in 25 mm glucose and no IGF-I. B, SMC expressing the siRNA-MMP-2 (MMP-2) or the empty vector control (EV) that had been grown in 5 mm glucose were plated (2 × 104 cells per well) in 24-well plates for 24 h to allow attachment. After an overnight incubation in SFM, they were then exposed to IGF-I (50 ng/ml) in DMEM plus 0.2% platelet-poor plasma. After an additional 48 h, cell number was determined by trypan blue staining and counting. **, P < 0.01 when the response of siRNA-MMP-2 (MMP-2) to IGF-I is compared with the response of the empty vector (EV) control cells (n = 3). There was no significant difference in the basal proliferation between SMC grown in 5 or 25 mm glucose. Cell numbers were 2.3 ± 0.3 × 104 when SMC were grown in high glucose in the absence of IGF-I for 24 h and 2.7 ± 0.4 × 104 when SMC were grown in normal glucose in the absence of IGF-I for 24 h. Hence, the proliferation response is expressed as fold increase over basal.
