Figure 2.
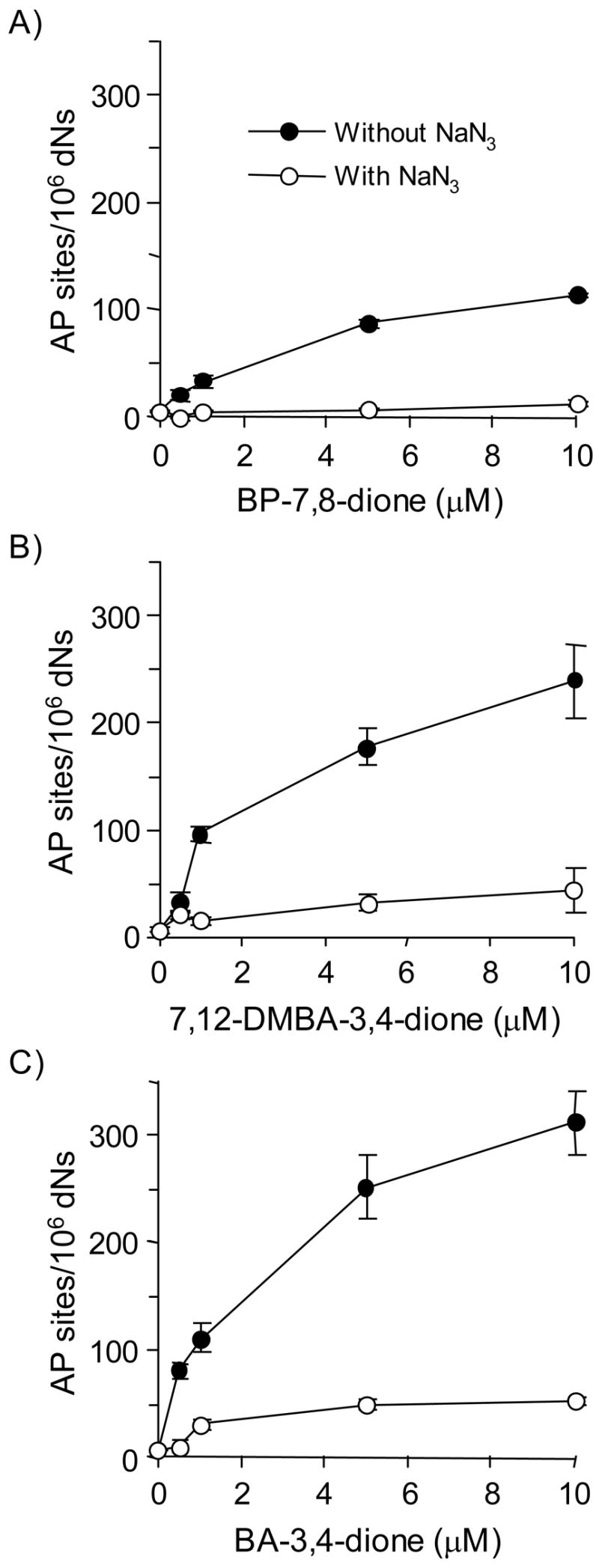
Detection of directly formed AP sites in PAH o-quinone-treated calf thymus DNA under redox-cycling conditions. (A) BP-7,8-dione, (B) 7,12-DMBA-3,4-dione and (C) BA-3,4-dione. See the Materials and methods for details. Kruskal-Wallis tests show that all three quinones had a significant effect on the AP sites generated (p = 0.0094, 0.0367 and 0.0093 for BP-7,8-dione, BA-3,4-dione and 7,12-DMBA-3,4-dione, respectively). Linear regression analysis showed that the concentration of all three quinones had a significant effect on the amount of AP sites (p <0.0001 for all three quinones). In each case, sodium azide blocked the formation of AP sites with p value < 0.0001 at all concentrations of PAH o-quinone tested.
