Fig. 1.
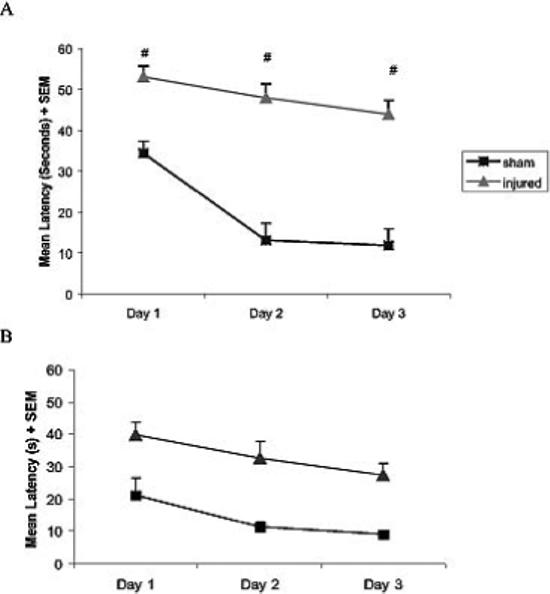
Acquisition and shift learning performance of rats in the Morris water maze (MWM). (A) Acquisition/Initial learning: Sham-injured and brain-injured rats were subjected to a visuospatial Morris water task at 4 weeks post-injury, showing the average of each training day (8 trials) per day. Brain-injury resulted in significant learning deficits over time in comparison to sham injury (# = p < 0.0001). (B) Platform relocation learning: The same rats were subjected to a relocated platform in the MWM at 8 weeks post-injury. Brain-injury significantly impaired the animals' ability to locate the hidden platform in comparison to sham-injury (p < 0.001). The mean latency to reach the hidden platform (+ SEM) of the training block at 4 and 8 weeks is shown.
