Figure 6.
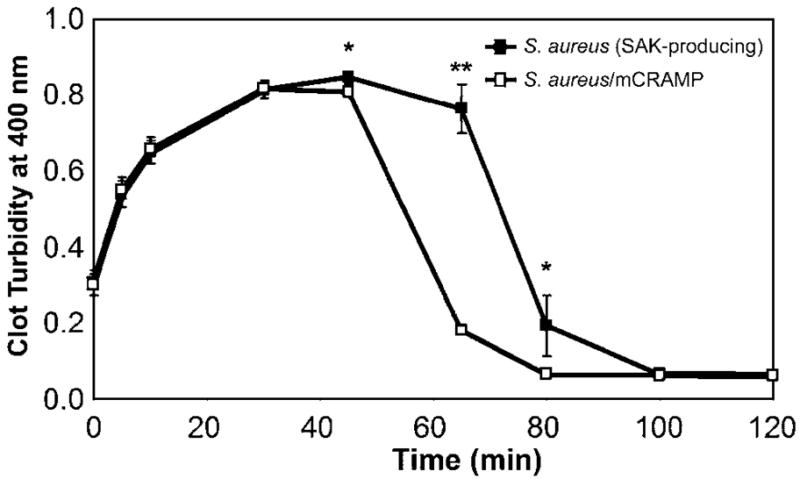
Augmentation of staphylokinase (SAK)–dependent fibrinolysis by cathelicidin (mCRAMP). Supernatants from stationary-phase cultures of SAK-producing Staphylococcus aureus were incubated alone or in the presence of mCRAMP (10 μg/mL) for 30 min at 37°C. To initiate fibrin clot formation, CaCl2 (2 mmol/L) and α-thrombin (1 nmol/L) were added to human fibrinogen (10 μmol/L), human plasminogen (500 nmol/L), and S. aureus supernatants or supernatant/mCRAMP mixtures. Fibrin clot formation and lysis were assessed by measuring changes in turbidity over time at 25°C as absorbance at 400 nm. Data are the mean ± SD of triplicate values and are representative of 3 independent experiments. **P < .001, *P = .05, Student’s t test.
