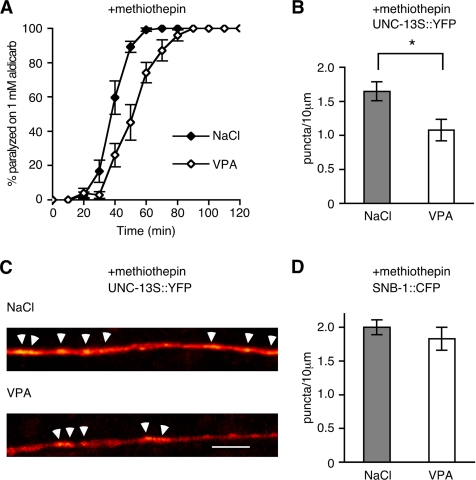
Figure 5.
VPA decreases UNC-13 accumulation but not synapse numbers. (A) The serotonin antagonist methiothepin causes animals to become hypersensitive to aldicarb-induced paralysis. This effect is reversed by exposure to VPA (on methiothepin and NaCl paralysis at 60 min is 99.2% ± 0.9 SEM, on methiothepin and VPA paralysis is 74.1 ± 5.9% SEM, p = 0.003, using unpaired Student's t test). (B and C) The serotonin antagonist methiothepin causes UNC-13::YFP to become punctate in a DAG-dependent manner (Nurrish et al., 1999), and this is suppressed by exposure to 12 mM VPA. In B, each data point represents mean ± SEM from 14 animals (p < 0.05, Student's t test). In C, digital images were converted from grayscale into a 32-color lookup table (ImageJ) to visualize pixel intensities. Arrows point to puncta counted in B. Bar, 10 μm. (D) The integral membrane protein SNB-1::CFP is enriched in synaptic vesicles; thus, it acts as a marker for synaptic vesicle release sites. VPA did not alter the density of SNB-1::CFP puncta.