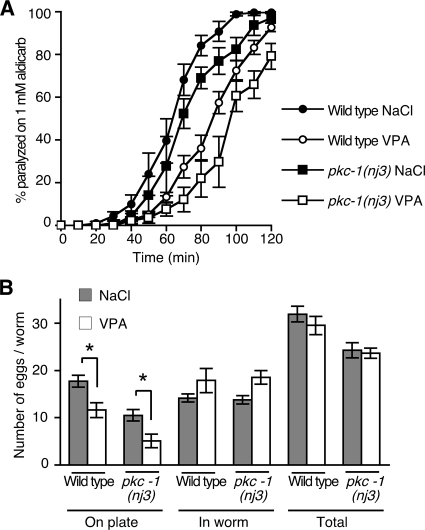
Figure 7.
VPA inhibits ACh release and egg laying in a pkc-1 mutant. (A) Levels of ACh release were measured by determining rates of paralysis in the presence of the acetylcholinesterase inhibitor aldicarb. pkc-1(nj3) mutant animals are resistant to aldicarb induced paralysis compared with wild type in the absence of salt (data not shown) and in the presence of 12 mM NaCl. Exposure to 12 mM VPA caused both wild-type and pkc-1(nj3) mutant animals to become resistant to aldicarb (For pkc-1(nj3), paralysis at 80 min on NaCl is 68.9 ± 5.0% SEM, on VPA 21.9 ± 8.7% SEM, p = 0.0008, using unpaired Student's t test). (B) Exposure to 6 mM VPA caused pkc-1(nj3) mutant animals to lay fewer eggs on the plate than animals exposed to 6 mM NaCl. Exposure to 6 mM VPA did not affect the total number of eggs produced (*p < 0.05, Student's t test).