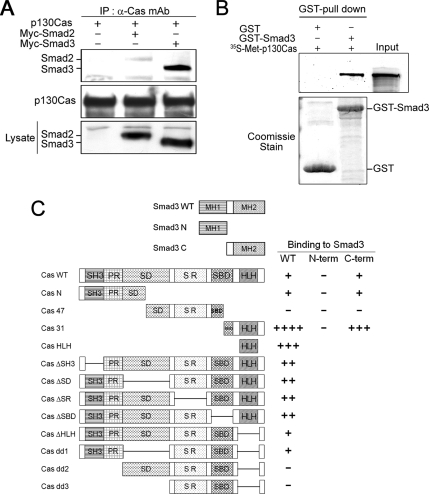
Figure 1.
p130Cas interacts directly with Smad3. (A) HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids, after which their lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-p130Cas mAb and immunoblotted with anti-Myc mAb. In this and all other experiments, the expression of proteins was determined by direct immunoblotting. (B) GST-Smad3 and GST were tested for their ability to directly interact with in vitro translated 35S-Met– labeled p130Cas. Equal amounts of GST or GST-Smad3 were used, as determined by Coomassie Blue staining (bottom). (C) Schematic representation of p130Cas and Smad3 deletion mutants, and the results of domain-mapping studies: Cas WT, wild-type p130Cas; Cas N, p130Cas N terminus; Cas 47, 47-kDa fragment of p130Cas; Cas 31, 31-kDa fragment p130Cas (Kook et al., 2000); Cas HLH, helix-loop-helix domain (Kim et al., 2004); ΔSH3, deletion of the SH3 domain; ΔSD, deletion of the substrate domain; ΔSR, deletion of the serine rich region; ΔSBD, deletion of the Src-binding domain; ΔHLH, deletion of the helix-loop-helix domain; dd1, deletion of the SD and HLH domain; dd2, deletion of the SH3, PR, and HLH domains; dd3, deletion of SH3, PR, SD, and HLH domains; Smad3 N, Smad3 N terminus; Smad3 C, linker region and C terminus of Smad3; − indicates a lack of detectable interaction; ++++ indicates a very strong interaction.