Figure 2.
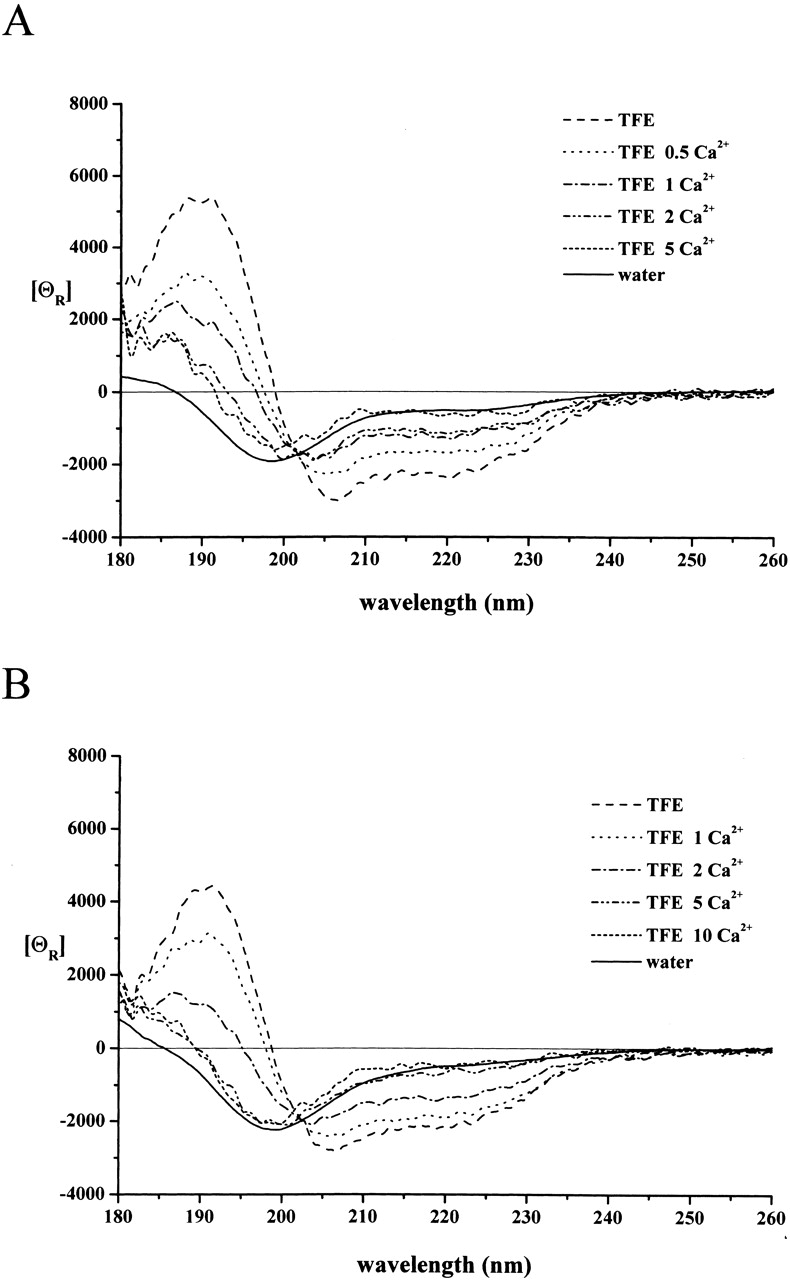
The effect of Ca2+ ions on the conformation of peptides A and C. The CD spectrum of peptide A (A) and peptide C (B) was recorded at 10 μM concentrations in TFE in the absence and presence of Ca2+ ions (given in molar equivalence). With both peptides, Ca2+ ions cause a conformational change toward the unstructured state observed in water. In the case of peptide A, the conformational transition occurs with a half-effective concentration that corresponds to 1 equivalent. With peptide C, the binding of Ca2+ is weaker; the half-effective stoichiometry is ~2 equivalents. For a comparison, the spectra in water, taken from Figure 1 ▶, are also shown.
