Table 1.
Structural statistics and root-mean-square deviation for 20 structures of S. pneumoniae CMP kinase
| Structural statisticsa | ≤SA> | ≤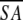 >r >r
|
| Rmsd from experimental distance restraints (Å)b | ||
| All (3100) | 0.014 ± 0.001 | 0.014 |
| Intraresidue (906) | 0.016 ± 0.001 | 0.016 |
| Sequential (777) | 0.017 ± 0.001 | 0.017 |
| Medium range (597) | 0.011 ± 0.001 | 0.010 |
| 0 Long range (712) | 0.010 ± 0.002 | 0.010 |
| Hydrogen bond (108) | 0.012 ± 0.001 | 0.011 |
| Rmsd from experimental torsional angle restraints (deg)c | ||
| φ and ξ angles (326) | 0.24 ± 0.02 | 0.25 |
| CNX potential energies (kcal mole−1) | ||
| Etot | 144 ± 5 | 140 |
| Ebond | 6 ± 0.3 | 6 |
| Eang | 85 ± 2 | 84 |
| Eimp | 7 ± 0.6 | 7 |
| Erepel | 12 ± 1 | 12 |
| Enoe | 33 ± 3 | 30 |
| Ecdih | 1 ± 0.2 | 1 |
| Rmsd from idealized geometry | ||
| Bonds (Å) | 0.00 ± 0.00 | 0.00 |
| Angles (deg) | 0.29 ± 0.00 | 0.29 |
| Impropers (deg) | 0.16 ± 0.01 | 0.15 |
| Cartesian coordinate rmsd (Å) | N, Cα, and C′ | All heavy |
≤SA> vs. ≤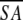 >d >d
|
1.04 ± 0.21 | 1.46 ± 0.19 |
≤SA> vs. ≤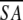 >e >e
|
0.74 ± 0.15 | 1.13 ± 0.12 |
a Where ≤SA> is the ensemble of 20 NMR-derived solution structures of S. pneumoniae CMP kinase; ≤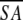 > is the mean atomic structure; ≤
> is the mean atomic structure; ≤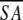 >r is the energy-minimized average structure. The CNX Frepel function was used to simulate van der Waals interactions using a force constant of 4.0 kcal mole−1 Å−4 with the atomic radii set to 0.8 times their CHARMM values (Brooks et al. 1983).
>r is the energy-minimized average structure. The CNX Frepel function was used to simulate van der Waals interactions using a force constant of 4.0 kcal mole−1 Å−4 with the atomic radii set to 0.8 times their CHARMM values (Brooks et al. 1983).
b Distance restraints were used with a square-well potential (Fnoe = 50 kcal mole−1 Å−2). Hydrogen bonds were given bounds of 1.8–2.4 Å (H−O) and 2.7–3.3 Å (N−O). No distance restraint was violated by more than 0.3 Å in any of the final structures.
c Torsional restraints were applied with values derived from an analysis of the C′, N, Cα, Hα, and Cβ chemical shifts using the TALOS program (Cornilescu et al. 1999). A force constant of 200 kcal mole−1 rad−2 was applied for all torsional restraints.
d Rmsd for the residues 16–234.
e Rmsd for the residues 16–161 and 208–234 in the core and substrate-binding domains.
