Figure 1. Accumulation of SKN-1 in intestinal nuclei is inhibited by DAF-2.
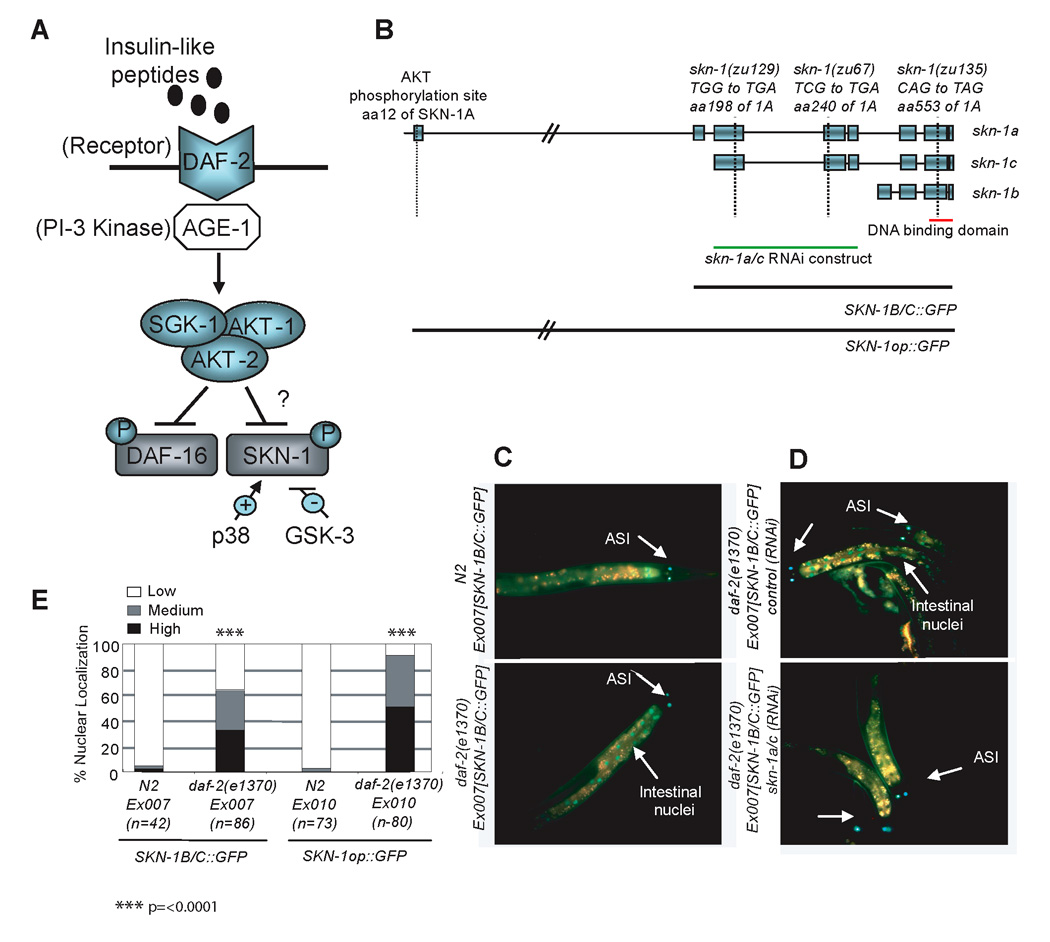
A) A partial schematic of C. elegans insulin-like signaling and our working model. B) skn-1 isoforms, alleles, and transgenes. The SKN-1A isoform is transcribed from an upstream operon promoter, and differs from SKN-1C by the addition of 90 amino acids at its N-terminus. SKN-1B and SKN-1C are each expressed from their own distinct upstream promoter (An and Blackwell, 2003; Bishop and Guarente, 2007). The skn-1(zu67), (zu129), and (zu135) mutations each create a premature stop codon (B. Bowerman, personal communication). Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) is fused to the C-terminus of SKN-1 in the transgenes indicated at the bottom. Strains that carry these and other transgenes are described in Table S2. The skn-1a/c RNAi construct includes only coding sequence, and targets both SKN-1A and SKN-1C, but does not alter the levels of SKN-1B in the ASI neurons (Bishop and Guarente, 2007). C) SKN-1::GFP accumulates in intestinal nuclei when DAF-2 activity is reduced. D) Intestinal expression of SKN-1B/C::GFP in daf-2(e1370) derives from SKN-1C. E) Quantification of SKN-1 intestinal nuclear accumulation. Here and in Figure 2, results of experiments performed on L4 larvae have been combined and scored as described in the supplementary methods and in (An and Blackwell, 2003; An et al., 2005). p values were derived from a chi2 test.
