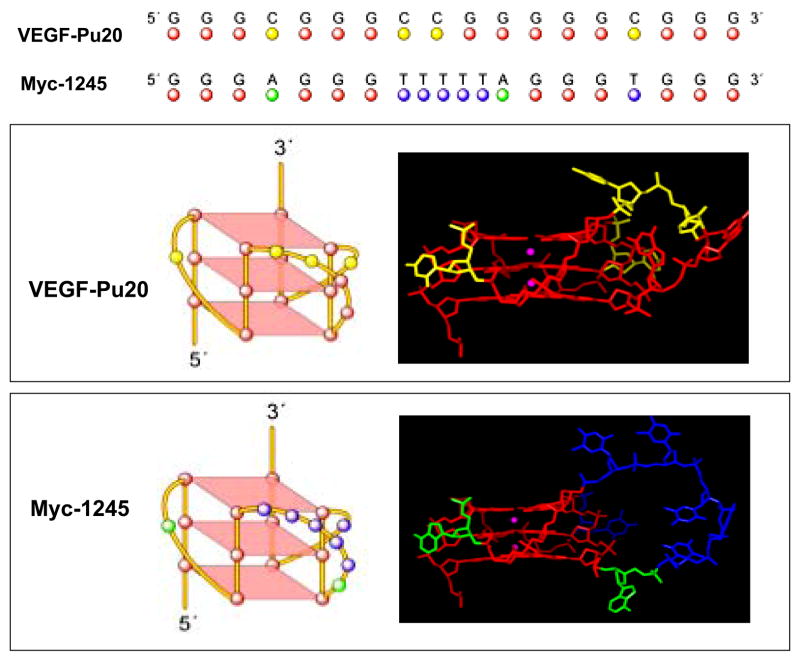
Figure 4.
Molecular modeling structures for G-quadruplexes formed by VEGF-Pu20 in comparison to the known folding pattern of myc-1245. Top, alignment of both sequences. Middle, schematic illustration (left panel) and molecular modeling structure (right panel) of the VEGF parallel quadruplex. Bottom, schematic illustration (left panel) and molecular modeling structure (right panel) of the myc-1245 parallel quadruplex. The structure of the human c-myc parallel quadruplex was used as a starting structure (35). Necessary replacements and deletions were done. Loop geometries were obtained as in the case of the human telomeric DNA parallel quadruplex (PDB code 1KF1) (34). Modeling was performed using the Biopolymer module with Insight II modeling software and charges, and potential types were assigned using Amber forcefield within Insight II. Structures were minimized using 2500 steps of Discover 3 minimization as described previously (42).