Figure 6. Dynein is important for targeting of p150Glued/Nip100 to the microtubule plus end.
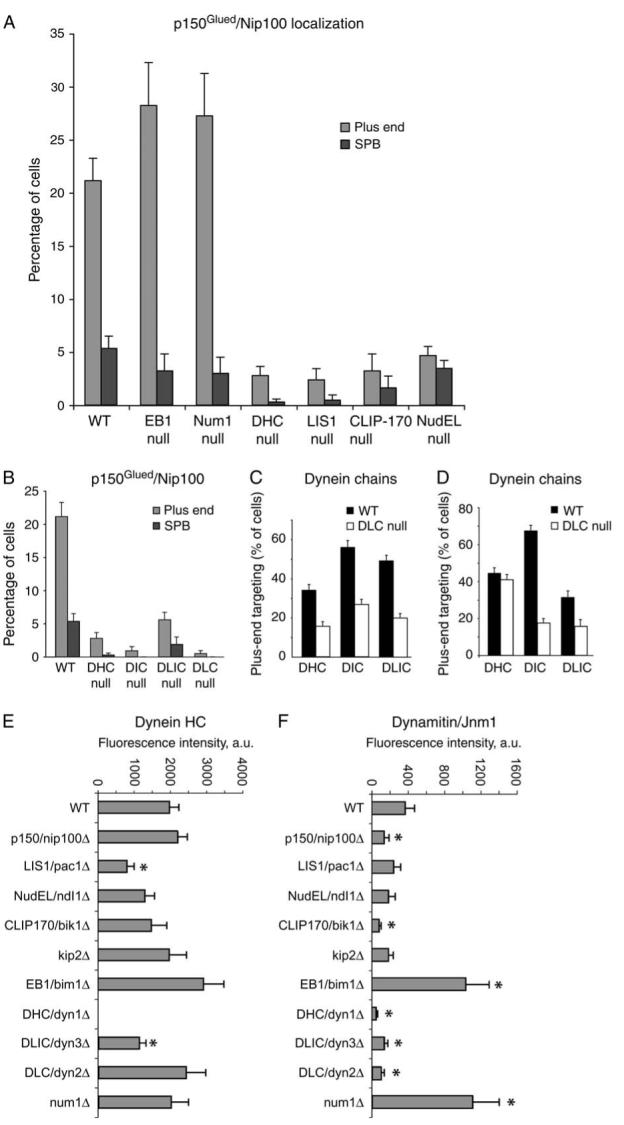
A and B) Percentage of cells with Nip100-GFP at a plus end or an SPB in various mutants. DHC, Dyn1. DIC, Pac11. DLIC, Dyn3. DLC, Dyn2. C) Plus-end targeting of GFP-tagged dynein chains in a DLC null mutant, dyn2Δ. D)Plus-end targeting of dynein chains in a DLIC null mutant, dyn3Δ. Dynein heavy chain and DIC require each other for stability and thus for targeting, and no dynein chains target to plus ends in the absence of DIC or intermediate chain. E and F) Fluorescence intensity of Dyn1-3GFP and Jnm1-tdimer2 at the plus end. Values are the means of the fluorescence intensity of the most bud-proximal cytoplasmic microtubule in G2/M cells expressing CFP-Tub1. Error bars denote standard error of the mean. Z-series images were collected for G2/M cells, identified by spindle length and grown in log-phase cultures. Microtubule ends were identified in the CFP-Tub1 image, and intensity measurements were taken from the corresponding plane of the GFP or tdimer2 stack. Asterisks mark results significantly different from wildtype (p < 0.05). Strain numbers and numbers of cells were as follows: A) WT, yJC4147, 369; EB1 null, yJC4177, 124; Num1 null, yJC4316, 301; DHC null, yJC4180, 361; LIS1 null, yJC4178, 210; CLIP-170 null, yJC4182, 124 and NudEL null, yJC4253, 581. B) WT, yJC4147, 369; DHC null, yJC4180, 361; DIC null, yJC5264, 222; DLIC null, yJC4314, 323 and DLC null, yJC43112, 211. C) DHC/WT, yJC2914, 261; DHC/DLC null, yJC4310, 195; DIC/WT, yJC3499, 242; DIC/DLC null, yJC4369, 280; DLIC/WT, yJC3369, 294 and DLIC/DLC null, yJC4367, 270. D) DHC/WT, yJC2914, 261; DHC/DLIC null, yJC4458, 291; DIC/WT, yJC3499, 242; DIC/DLIC null, yJC5266, 235; DLC WT, yJC4555, 166 and DLC/DLIC null, yJC4951, 96. E and F) WT, yJC5652, 23; nip100Δ, yJC5661, 32; pac1Δ, yJC5664, 22; ndl1Δ, yJC5665, 20; bik1Δ, yJC5662, 23; kip2Δ, yJC5663, 13; bim1Δ, yJC5678, 15; dyn1Δ, yJC5669, 16; dyn3Δ, yJC5667, 21; dyn2Δ, yJC5668, 12 and num1Δ, yJC5666, 17.
