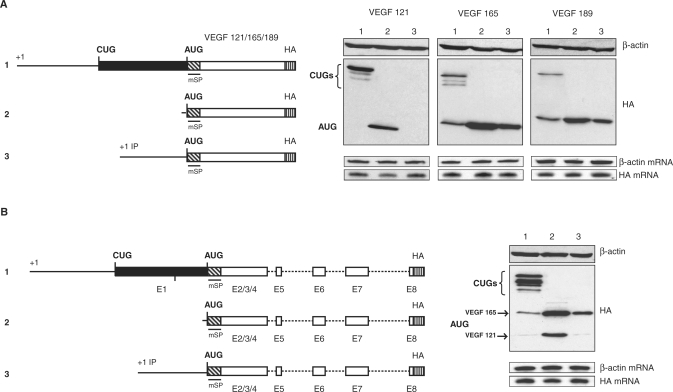
Figure 3.
Role of the VEGF-A 5′UTR on alternative translation initiation control. (A) Schematic representation of the constructs used for transfection experiments: constructs, encoding each isoform and the VEGF minigene, beginning at the main promoter (p121mSPHA, p165mSPHA, p189mSPHA and pminiVEGF, numbered 1), constructs beginning 24 nucleotides upstream from the AUG (pAUG121mSPHA, pAUG165mSPHA, pAUG189mSPHA and pAUGminiVEGF, numbered 2), and constructs beginning at the internal promoter start site +633 (pIP121mSPHA, pIP165mSPHA, pIP189mSPHA and pIPminiVEGF numbered 3). (B) Each plasmid were transiently transfected into HeLa cells. Their expression was analyzed by western immunoblotting using an anti-HA antibody. An anti-β-actin was used to control protein loading. The constructs 1 give rise to the VEGF and the L-VEGF proteins and the other constructs encode only the AUG initiated VEGF proteins. RPA analyses were performed to normalize transfection with a vector specific probe to quantify mRNA and with a β-actin probe to control RNA quantity.