Abstract
Many picornaviruses cause a dramatic decrease in the translation of cellular mRNAs in the infected cell, without affecting the translation of their own RNA. Specific proteolysis of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4 gamma occurs during infection with rhinoviruses, enteroviruses, and aphthoviruses, apparently leading to an inability of the ribosomes to bind capped mRNAs. Cleavage of eIF-4 gamma in human rhinoviruses and enteroviruses is carried out by the viral 2A proteinase; in aphthoviruses (i.e., foot-and-mouth disease viruses), the leader proteinase is responsible for this reaction. We describe here the purification to homogeneity of the Lb form of the leader proteinase expressed in Escherichia coli. The primary cleavage products of eIF-4 gamma obtained in vitro with purified leader or 2A proteinase are electrophoretically indistinguishable from those found during infection in vivo. However, additional proteolysis products of eIF-4 gamma are observed with the leader proteinase and the human rhinovirus type 2 2A proteinase in vitro. The cleavage site of the leader proteinase in eIF-4 gamma from rabbit reticulocyte was determined by sequencing the purified C-terminal cleavage product by automated Edman degradation. The cleavage site is between Gly-479 and Arg-480 and thus differs from that of rhinovirus and enterovirus 2A proteinases, which cleave between Arg-486 and Gly-487.
Full text
PDF


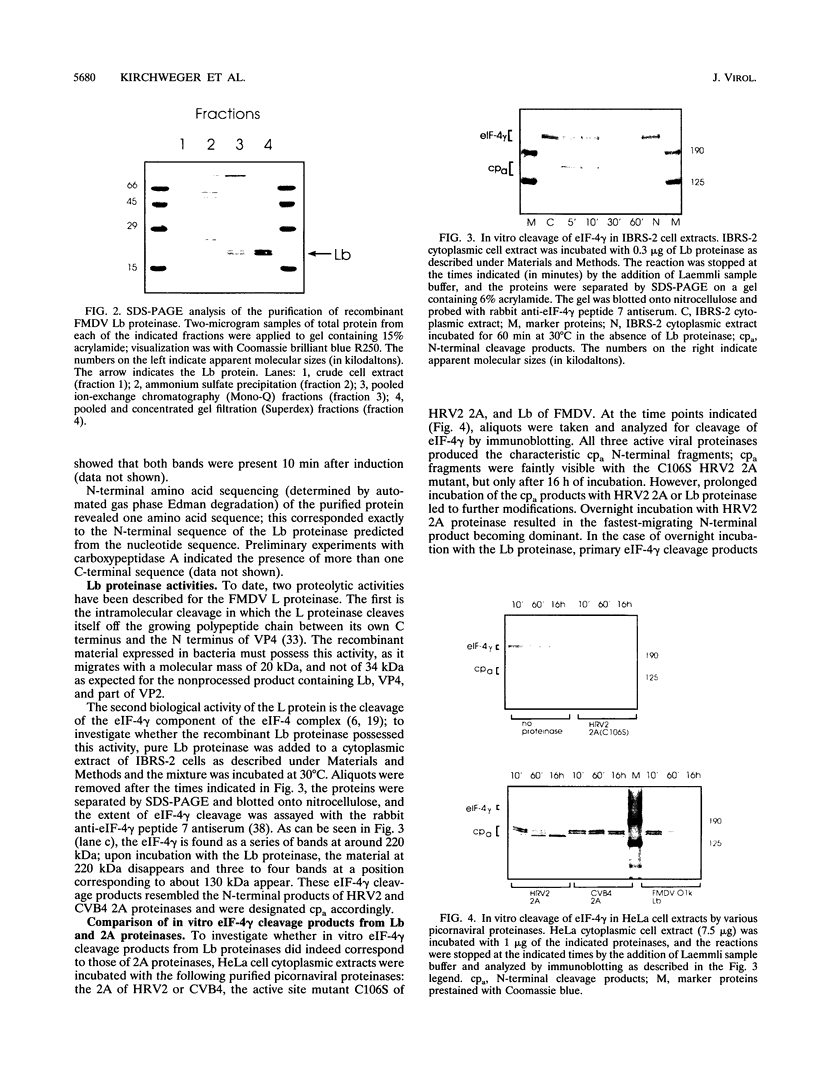
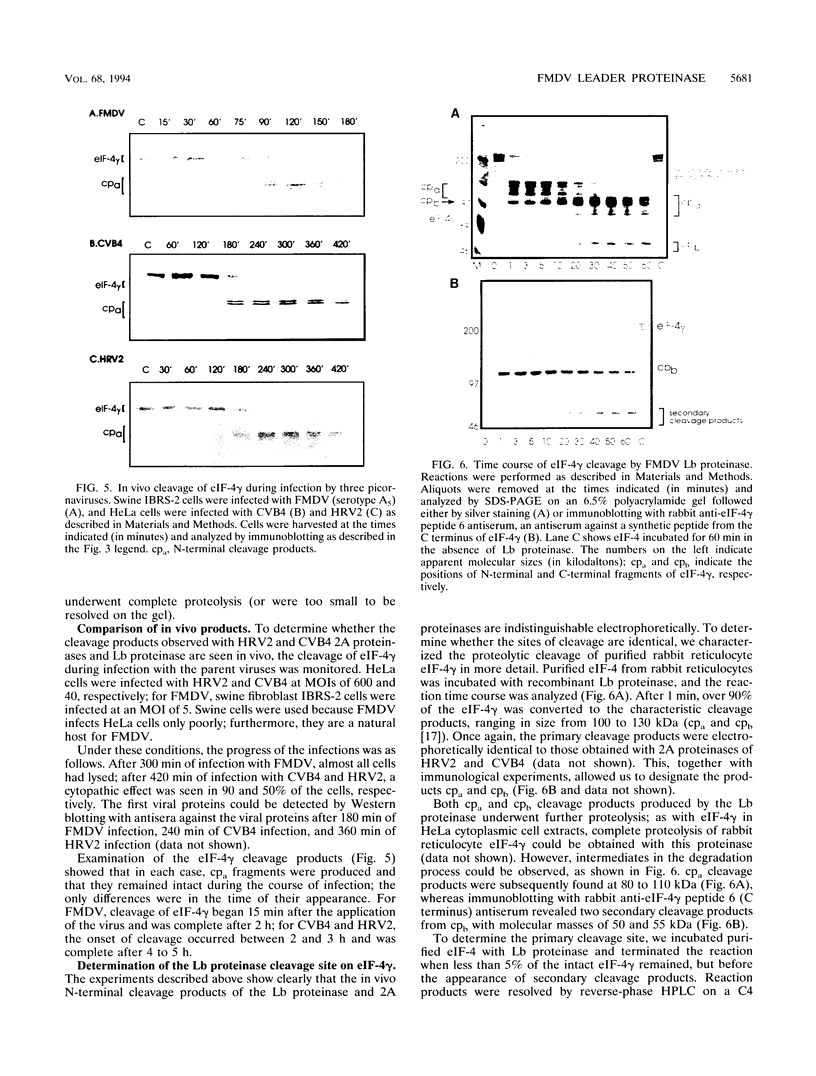



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson S. D., Herbert E., Kemp S. F. Effects of hemin and other porphyrins on protein synthesis in a reticulocyte lysate cell-free system. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jun 14;42(2):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argos P., Kamer G., Nicklin M. J., Wimmer E. Similarity in gene organization and homology between proteins of animal picornaviruses and a plant comovirus suggest common ancestry of these virus families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7251–7267. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazan J. F., Fletterick R. J. Viral cysteine proteases are homologous to the trypsin-like family of serine proteases: structural and functional implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7872–7876. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck E., Forss S., Strebel K., Cattaneo R., Feil G. Structure of the FMDV translation initiation site and of the structural proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 25;11(22):7873–7885. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.22.7873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonneau A. M., Sonenberg N. Proteolysis of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex is not sufficient for complete inhibition of host cell protein synthesis after poliovirus infection. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):986–991. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.986-991.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devaney M. A., Vakharia V. N., Lloyd R. E., Ehrenfeld E., Grubman M. J. Leader protein of foot-and-mouth disease virus is required for cleavage of the p220 component of the cap-binding protein complex. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4407–4409. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4407-4409.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Blinov V. M., Donchenko A. P. Poliovirus-encoded proteinase 3C: a possible evolutionary link between cellular serine and cysteine proteinase families. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):253–257. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbalenya A. E., Koonin E. V., Lai M. M. Putative papain-related thiol proteases of positive-strand RNA viruses. Identification of rubi- and aphthovirus proteases and delineation of a novel conserved domain associated with proteases of rubi-, alpha- and coronaviruses. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):201–205. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81034-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hambidge S. J., Sarnow P. Translational enhancement of the poliovirus 5' noncoding region mediated by virus-encoded polypeptide 2A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10272–10276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. J., Howell M. T., Kaminski A. The novel mechanism of initiation of picornavirus RNA translation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Dec;15(12):477–483. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90302-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joshi B., Yan R., Rhoads R. E. In vitro synthesis of human protein synthesis initiation factor 4 gamma and its localization on 43 and 48 S initiation complexes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):2048–2055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleina L. G., Grubman M. J. Antiviral effects of a thiol protease inhibitor on foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol. 1992 Dec;66(12):7168–7175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.12.7168-7175.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kräusslich H. G., Nicklin M. J., Toyoda H., Etchison D., Wimmer E. Poliovirus proteinase 2A induces cleavage of eucaryotic initiation factor 4F polypeptide p220. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2711–2718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2711-2718.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamphear B. J., Panniers R. Cap binding protein complex that restores protein synthesis in heat-shocked Ehrlich cell lysates contains highly phosphorylated eIF-4E. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5333–5336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamphear B. J., Yan R., Yang F., Waters D., Liebig H. D., Klump H., Kuechler E., Skern T., Rhoads R. E. Mapping the cleavage site in protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4 gamma of the 2A proteases from human Coxsackievirus and rhinovirus. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19200–19203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebig H. D., Ziegler E., Yan R., Hartmuth K., Klump H., Kowalski H., Blaas D., Sommergruber W., Frasel L., Lamphear B. Purification of two picornaviral 2A proteinases: interaction with eIF-4 gamma and influence on in vitro translation. Biochemistry. 1993 Jul 27;32(29):7581–7588. doi: 10.1021/bi00080a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Grubman M. J., Ehrenfeld E. Relationship of p220 cleavage during picornavirus infection to 2A proteinase sequencing. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4216–4223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4216-4223.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd R. E., Jense H. G., Ehrenfeld E. Restriction of translation of capped mRNA in vitro as a model for poliovirus-induced inhibition of host cell protein synthesis: relationship to p220 cleavage. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2480–2488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2480-2488.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medina M., Domingo E., Brangwyn J. K., Belsham G. J. The two species of the foot-and-mouth disease virus leader protein, expressed individually, exhibit the same activities. Virology. 1993 May;194(1):355–359. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C. Mechanism and regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Jun;56(2):291–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.2.291-315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez L., Carrasco L. Lack of direct correlation between p220 cleavage and the shut-off of host translation after poliovirus infection. Virology. 1992 Jul;189(1):178–186. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90693-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Regulation of eukaryotic protein synthesis by initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3017–3020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V., Newton S. E., Rowlands D. J., Clarke B. E. All foot and mouth disease virus serotypes initiate protein synthesis at two separate AUGs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3305–3315. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skern T., Sommergruber W., Blaas D., Gruendler P., Fraundorfer F., Pieler C., Fogy I., Kuechler E. Human rhinovirus 2: complete nucleotide sequence and proteolytic processing signals in the capsid protein region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2111–2126. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommergruber W., Ahorn H., Klump H., Seipelt J., Zoephel A., Fessl F., Krystek E., Blaas D., Kuechler E., Liebig H. D. 2A proteinases of coxsackie- and rhinovirus cleave peptides derived from eIF-4 gamma via a common recognition motif. Virology. 1994 Feb;198(2):741–745. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommergruber W., Ahorn H., Zöphel A., Maurer-Fogy I., Fessl F., Schnorrenberg G., Liebig H. D., Blaas D., Kuechler E., Skern T. Cleavage specificity on synthetic peptide substrates of human rhinovirus 2 proteinase 2A. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 5;267(31):22639–22644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommergruber W., Zorn M., Blaas D., Fessl F., Volkmann P., Maurer-Fogy I., Pallai P., Merluzzi V., Matteo M., Skern T. Polypeptide 2A of human rhinovirus type 2: identification as a protease and characterization by mutational analysis. Virology. 1989 Mar;169(1):68–77. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Poliovirus translation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;161:23–47. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-75602-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E. E., Hershey J. W., Ehrenfeld E. Eukaryotic initiation factor 3 is required for poliovirus 2A protease-induced cleavage of the p220 component of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9529–9533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyckoff E. E., Lloyd R. E., Ehrenfeld E. Relationship of eukaryotic initiation factor 3 to poliovirus-induced p220 cleavage activity. J Virol. 1992 May;66(5):2943–2951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.5.2943-2951.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan R., Rychlik W., Etchison D., Rhoads R. E. Amino acid sequence of the human protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4 gamma. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):23226–23231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








