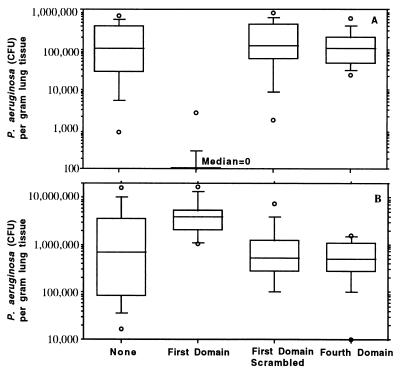
Figure 4.
Effect of addition of synthetic peptides to the bacterial inoculum on P. aeruginosa infection in neonatal mice. (A) Amount of P. aeruginosa internalized by lung cells 24 hr after infection. (B) Total amount of P. aeruginosa found in lungs 24 hr after infection. Box plots indicate (from bottom to top) the 10th, 25th, 50th (median), 75th, and 90th percentiles. Circles above or below the 90th or 10th percentile indicate individual points outside this range. There were 12–14 total lung samples used in each group. For both groups of comparisons (A and B), the overall differences were significant at P < 0.001 using the Kruskal–Wallis nonparametric ANOVA test, and the difference between the group receiving the first-domain peptide and the other three groups was significant at P < .001 using the Dunn procedure for pairwise comparisons.