Fig. 4.
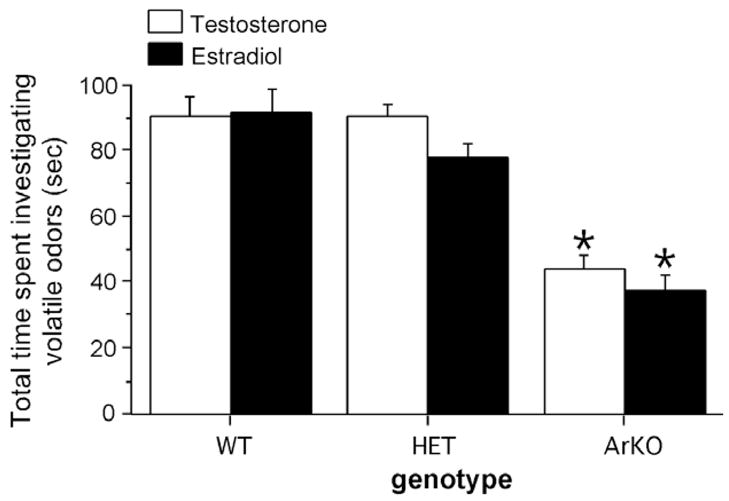
Total time spent investigating volatile odors by female wild-type (WT), heterozygous (HET), and aromatase knockout (ArKO) mice when given the choice between volatile body odors from an intact male versus those from an estrous female in a Y-maze. All female subjects were ovariectomized in adulthood and first tested for their odor preferences when receiving testosterone and then when receiving estradiol. *p < 0.05 compared to WT and HET females. Data shown are means ± SEM of two successive tests.
