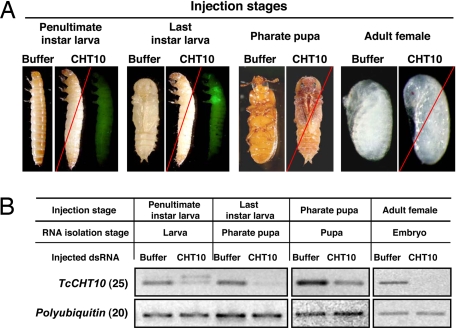
Fig. 2.
Effect of dsRNA for TcCHT10 on embryonic, larval, pupal, and adult development and egg hatch of Tribolium. The Pig-23 strain that has an EGFP tag to identify last instar larvae was used in this experiment. (A) dsRNA for TcCHT10 (200 ng per insect, n = 20) was injected into penultimate- or last-instar larvae, pharate pupae, or adult females as indicated above each image. All TcCHT10 dsRNA-injected animals died at the ensuing molt. Terminal phenotypes are shown. The left two sets of images (injections into penultimate and last instar larvae) show the same two individuals viewed microscopically under visible light (specimen on the left within the image labeled CHT10) and after excitation at 480 nm and monitoring emission at 510 nm to view the EGFP fluorescence (specimen on the right within the image labeled CHT10). When last instar larvae were injected with dsRNA for TcCHT10 (note EGFP fluorescence in wing imaginal discs), death occurred at the pupal stage with the larval cuticle still loosely attached to the posterior abdomen. The pharate pupa specimen labeled CHT10 (third image from the right) shows a typical terminal phenotype of insects injected at the pharate pupal stage. The far right image labeled CHT10 shows the embryos inside eggs laid by adult females injected with dsRNA for TcCHT10. These embryos are fully developed but failed to hatch. (B) Effect of buffer or dsRNA for TcCHT10 on transcript levels. Three to 4 days after injection, four insects from each treatment were collected for total RNA preparation and cDNAs were prepared and used as templates for RT-PCR. The number of RT-PCR cycles is indicated in parentheses except for egg samples (Right), in which RT-PCR was carried for 25 cycles with polyubiquitin primers and 30 cycles with TcCHT10 primers. The appearance of a larger band in some samples is attributable to contamination of RNA preparations with pre-mRNA for the target gene. The increase in size of the PCR product is consistent with the presence and size of a known intron between the two primer-binding sites.