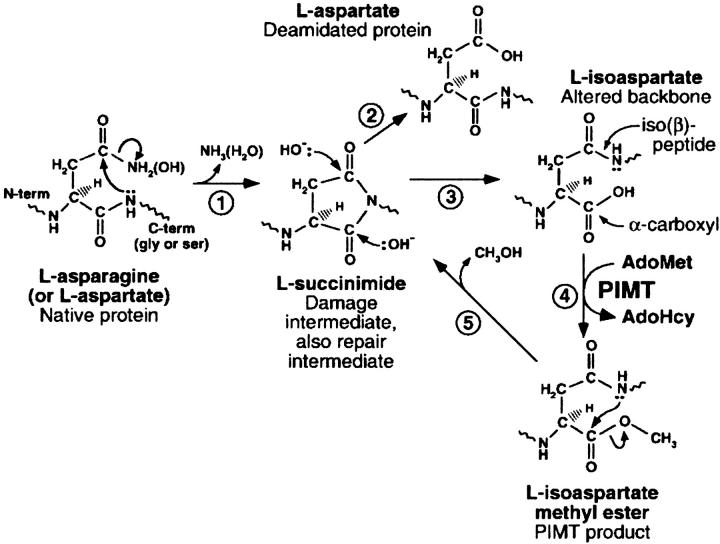
Fig. 1.
Protein deamidation, isoAsp formation, and the repair cycle catalyzed by PIMT. 1. Protein deamidation/dehydration at the susceptible residue in the native protein. 2. Hydrolysis of the intermediate succinimide to form L-aspartate. 3. Hydrolysis of the intermediate succinimide to form L-isoaspartate. 4. O-methylation by PIMT. 5. Release of methanol forms the L-succinimide intermediate. (Reproduced from Skinner et al. (2000), with permission of Elsevier Science.)