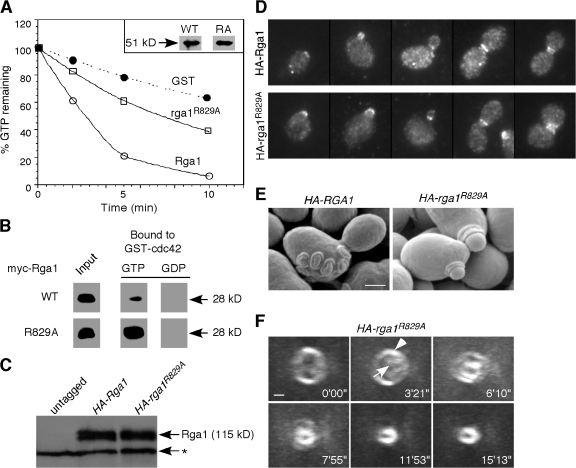
Figure 2.
The role of Rga1 in polarity axis determination depends on its Cdc42-GAP activity. (A) GAP assays. Cdc42 prebound to γ-[32P]GTP was incubated with GST, the GST-Rga1 GAP domain, or the same domain containing the R829A mutation, and radioactivity remaining bound to Cdc42 is plotted against time of incubation. The inset shows that similar amounts of wild-type and mutant GAP domains were used in the assay. This GAP assay is representative of three experiments with consistent results. (B) Binding assays. Recombinant myc-tagged Rga1 or rga1R829A GAP domains were incubated with bead-bound recombinant GST-cdc42Q61L (GTP-bound) or GST-cdc42T17N (GDP-bound) to assess binding. (C) HA-Rga1 and HA-rga1R829A are expressed at similar levels. Protein samples were prepared from YZT194 (HA-RGA1) and YZT195 (HA-rga1R829A). The asterisk indicates a cross-reacting protein with the HA-antibody in yeast extracts. (D) HA-Rga1 and HA-rga1R829A display similar localization patterns in the cell cycle. Strains YZT194 and YZT195 were grown to exponential phase in YM-P medium at 23°C and examined by immunofluorescence using an anti-HA antibody. (E) SEM observation of bud scars of strains YZT194 and YZT195. (F) Visualization of new septin ring formation in live cells of strain YZT198 (HA-rga1R829A CDC3-GFP) by 3D time-lapse microscopy. Eight out of nine cells were observed to form a new septin ring within the old ring. The arrowhead indicates the old septin ring; the arrow indicates the new septin ring. Bars, 1 μm.