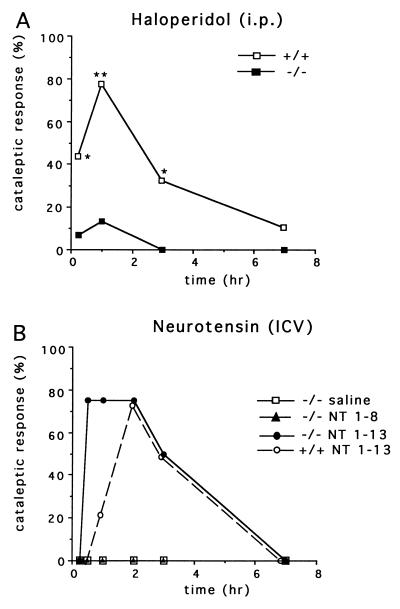
Figure 4.
The cataleptic response to haloperidol is significantly attenuated in RIIβ−/− mice, but they remain responsive to centrally administered NT. (A) Catalepsy was measured 15 min, 1 h, 3 h, and 7 h following administration of haloperidol (4 mg/kg, i.p.) in wild-type controls (n = 9) and RIIβ−/− (n = 15). Graph represents the percent of mice exhibiting catalepsy. Comparisons between groups were determined using Mann–Whitney U test; ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01. (B) Catalepsy was measured in RIIβ−/− (n = 4) mice at various times following administration of active NT 1–13, inactive NT 1–8, or saline. Wild-type mice (n = 4) were injected with the active NT 1–13 as a control.