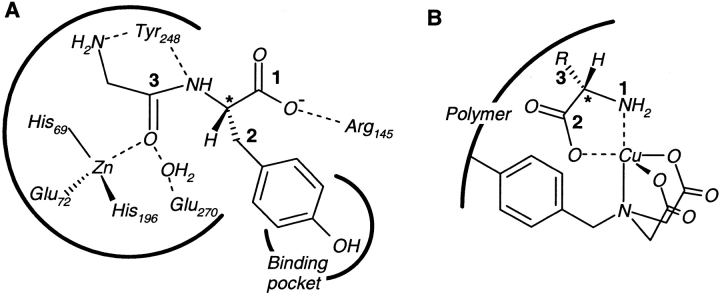
Fig. 2.
Multiple interactions between receptor sites and substrate locations. (A) In the binding of the enzyme carboxypeptidase A to glycyl-l-tyrosine (an asterisk marks the chiral center), the free amino group of glycine and the amide functionality together constitute a single substrate location, interacting with multiple binding groups on a large part of the enzyme's binding surface. (B) In ligand-exchange adsorbents, a transition metal ion (Cu2+) is immobilized via a metal chelating ligand. The amino and carboxylate groups form two distinct substrate locations, interacting with the same metal ion.