Fig. 1.
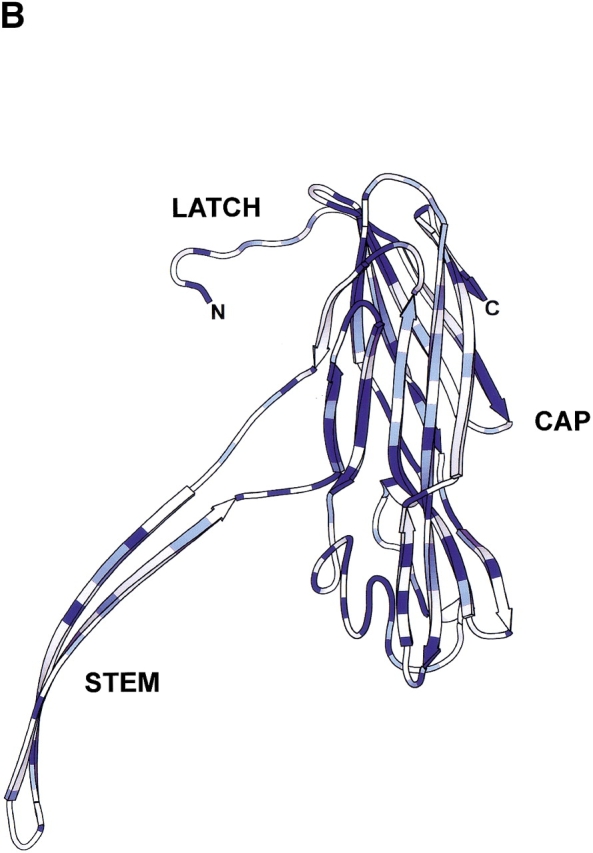
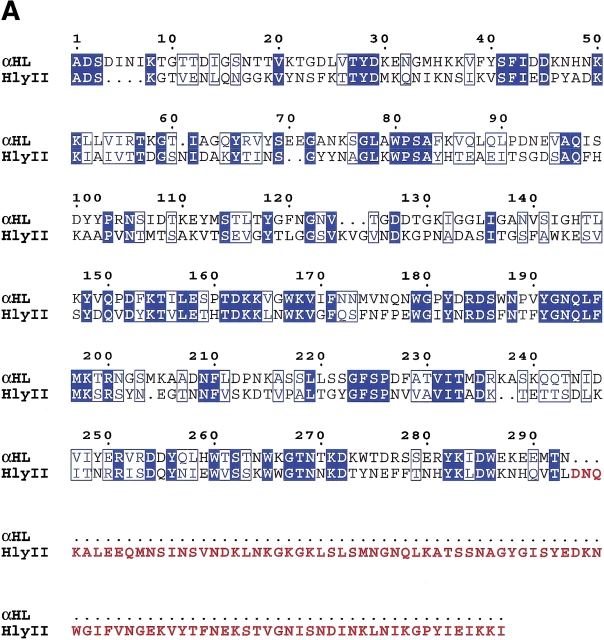
Comparison of Bacillus hemolysin II and staphylococcal α-hemolysin. (A) Primary sequence alignment of Bacillus cereus hemolysin II (HlyII) and staphylococcal α-hemolysin (αHL). Residues highlighted with a blue background are identical, while similar residues (Blosum62 similarity scoring matrix; Henikoff and Henikoff 1992) are shown as blue characters. The 94 residue C-terminal extension of HlyII is shown in maroon characters; it is the portion that was deleted to form the truncation mutant HlyII(ΔCT). The figure was generated using ClustalW 1.81 (Thompson et al. 1994) and rendered using ESPript 2.0 (Gouet et al. 1999). (B) Structure of one protomer taken from the crystal structure of the αHL heptamer (7aHL.pdb). Areas in dark blue and light blue correspond to identical and similar residues, respectively, as shown in (A). The image was created with SPOCK 6.3 (Christopher 1998) and rendered with Molscript (Kraulis 1991).