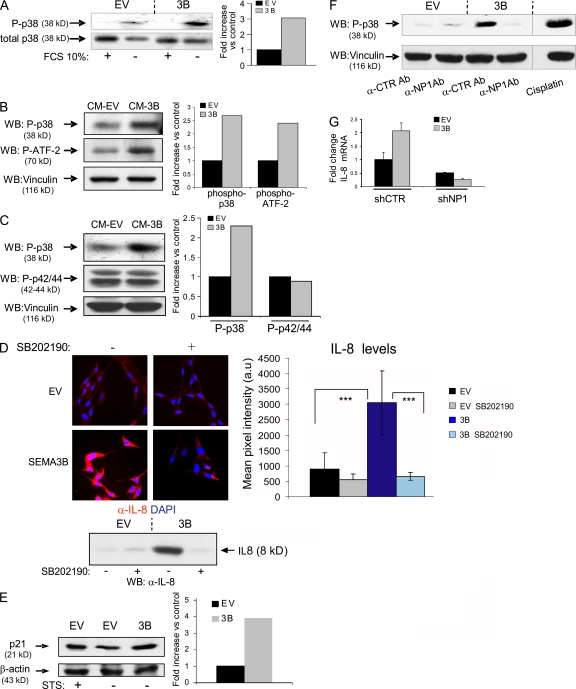
Figure 8.
p38–MAPK signaling elicited by SEMA3B mediates IL-8 induction. (A) Immunoblotting analysis to reveal phospho-p38 protein levels in MDA-MB435 tumor cells expressing SEMA3B (or EV controls), grown in the presence or absence of 10% FBS for 48 h. Results are displayed as fold induction of the phosphorylated/total p38 ratio in SEMA3B cells versus controls, as measured by densitometric analysis. (B) Serum-starved MDA-MB435 cells were treated for 30 min with CM collected from SEMA3B or EV control cells. The levels of phospho-p38 and phospho–ATF-2 were analyzed in protein lysates by immunoblotting. The same filter was furthermore decorated to reveal vinculin, providing loading controls. Plotted values indicate fold increase of the phosphorylated p38/vinculin or ATF2/vinculin ratios in SEMA3B-treated cells versus controls. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of A549 cells treated as in B with SEMA3B or EV control CM. Filters were probed to reveal phospho-p38, phospho-p42/44–MAPK, and vinculin levels (as loading control). The graph shows fold increase of the phosphorylated p38/vinculin or phospho-p42/44–MAPK/vinculin ratios in SEMA3B-treated cells versus controls. (D) MAB208 antibody was used to detect IL-8 expression by immunofluorescence (top) or by Western blotting (bottom) in SEMA3B-expressing and control cells grown in the absence of serum for 48 h, in the presence or absence of 10 μM of the selective p38–MAPK inhibitor SB202190. Micrographs were acquired with a bioimager (Pathway; BD Biosciences) and quantified by Autovision 1.5 (10 images per each data point). Results are displayed as mean ± SD. ***, P < 0.001. (E) CDKI p21 expression was detected by Western blotting in A549 cells, transduced with SEMA3B or EV control, upon serum starvation (48 h in 1% FCS). Cells treated with 20 nM staurosporin (STS) for 24 h provided a positive control for p21 activation. β-Actin levels provided a reference for protein loading. Plotted values indicate fold induction of the p21/β-actin ratio. (F) A549 cells were serum starved for 24 h and then treated for 30 min with CM from SEMA3B or EV control cells in the presence of 20 ng/ml anti-NP1 blocking antibody or the unrelated antibody anti–VSV-G. Cells treated with 20 μm cisplatin for 2 h provided a positive control for p38 activation. The levels of phospho-p38 and vinculin (as loading control) were analyzed in protein lysates by immunoblotting. (G) Consistent with a previous report, many tumor cells could not survive RNAi-mediated knock down of NP1 (reference 65); however, we managed to stably express NP1-targeted shRNAs (shNP1) in HeLa cells previously transduced with SEMA3B or EV (Fig. 5 B). Real-time PCR analysis indicated that NP1 expression levels were knocked down to 20% compared with cells transduced with unrelated sequences (shCTR; not depicted). Notably, SEMA3B autocrine stimulation was unable to up-regulate IL-8 levels in NP1-deficient cells, indicating the requirement for this receptor in the signaling pathway. The graph shows fold increase of expression relative to control cells. Data shown are the mean ± SEM.