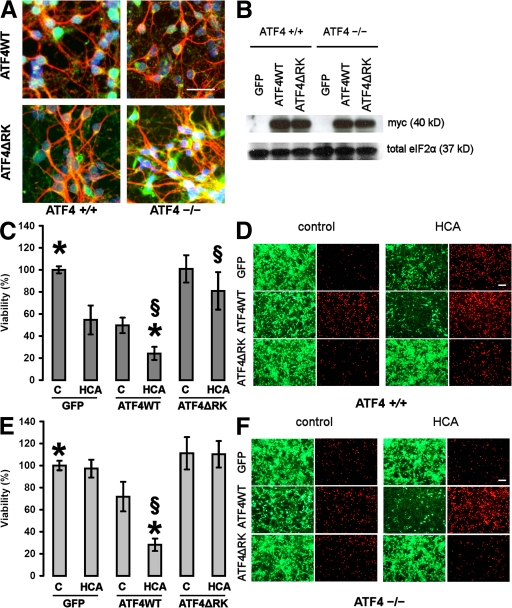
Figure 5.
Overexpression of ATF4WT restores sensitivity to oxidative stress and reduces neuronal viability itself. (A) Representative immunocytochemistry of ATF4+/+ and ATF4−/− cortical neurons infected with the adenoviral constructs ATF4WT and ATF4ΔRK. Neurons were stained with antibodies against myc (green) and MAP2 (red), and were counterstained with Hoechst dye (blue). Bar, 50 μm. (B) Whole-cell extracts obtained from both ATF4+/+ and ATF4−/− neurons infected with GFP, ATF4WT, and ATF4ΔRK were separated using gel electrophoresis and immunodetected using an antibody directed against the myc tag. Total eIF2α was monitored as a loading control. (C) ATF4+/+ cortical neurons were infected with GFP, ATF4WT, and ATF4ΔRK adenoviruses at an MOI of 100. 24 h after infection, neurons were treated with vehicle control (shown as C) or 10 mM HCA. 24 h later, cell viability was determined using the MTT assay. The graph depicts mean (compared with control) ± SD calculated from four separate experiments for each group (n = 45). P < 0.05 by the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test from untreated ATF4WT-overexpressing neurons (*) and from HCA-treated neurons overexpressing GFP (§). (D) Live/dead assay. Bar, 50 μm. (E) ATF4−/− cortical neurons were infected with GFP, ATF4WT, and ATF4ΔRK adenoviruses at an MOI of 100. 24 h after infection, neurons were treated with vehicle control (shown as C) or 10 mM HCA. 24 h later, cell viability was determined using the MTT assay. The graph depicts mean (compared with control) ± SD calculated from four separate experiments for each group (n = 28). P < 0.05 by the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's multiple comparisons test from untreated ATF4WT-overexpressing neurons (*) and from HCA-treated neurons overexpressing GFP (§). (F) Live/dead assay. Bar, 50 μm.