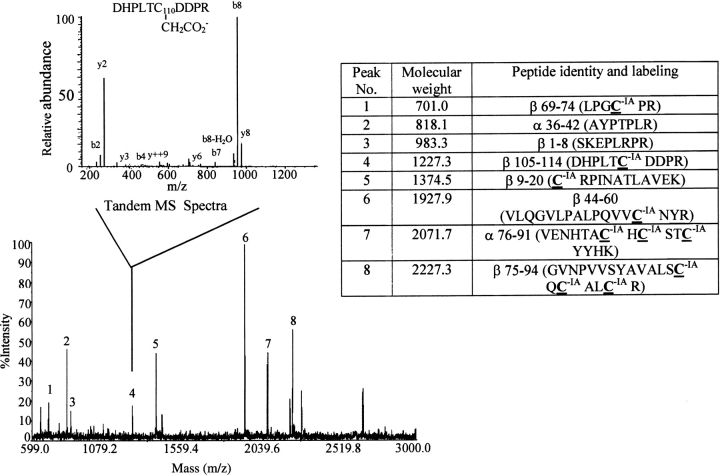
Fig. 3.
Cysteine residues identified by MS following reduction and alkylation of hCG. hCG subunit combination was carried out in the presence of VP, and the proteins then were reduced and alkylated by IA (VP > IA). Modification by VP would identify cysteines in disulfides that had broken during subunit combination. After subunit combination had been completed, the proteins were reduced and cysteine residues in disulfides that had not broken during subunit combination were alkylated with IA. As seen here, there was no VP incorporation into cysteine residues during subunit combination. This study was repeated in this and in a reciprocal fashion (not shown) during which IA was used to detect breaking of cysteines during subunit combination and VP was used to label all cysteines after the proteins had been completely reduced (IA > VP). In neither case did we observe alkylation of cysteines during subunit combination. The large spectrum was obtained by MALDI-TOF; the inset shows a tandem mass spectrum obtained for peak number 4. The table illustrates the amino acid sequences of all peptides labeled on the MALDI-TOF spectrum that were identified by tandem mass spectrometry.