Fig. 2.
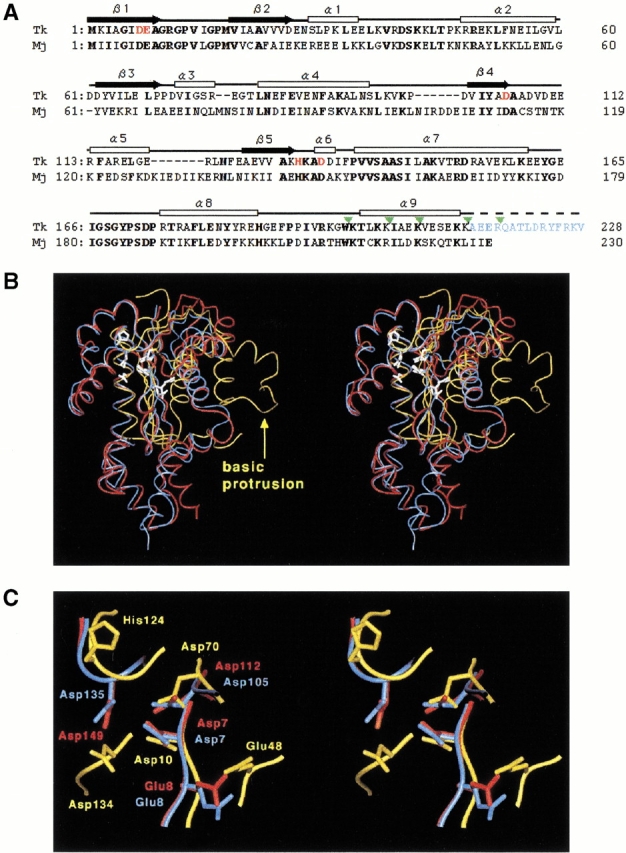
(A) Amino acid sequence alignment of Tk-RNase HII (Tk) and Mj-RNase HII (Mj) based on the comparison of their three-dimensional structures. The range of the secondary structures of Tk-RNase HII are shown above the sequence (white box for α-helix and black arrow for β-strand). Bold letters indicate amino acid residues conserved between the two proteins. The amino acid residues shown in red represent the mutated residues in the present study. The amino acid residues shown in blue are the truncated residues 214–228 in Tk-RNase HII-213. The truncation sites are indicated by green triangles. (B) Stereodiagram of the structures of Tk-RNase HII-213 (blue), Mj-RNase HII (red), and Ec-RNase HI (yellow). Root mean square displacements of the superimposition on the Tk-RNase HII structure are 1.2 Å for the 190 Cα atoms of Mj-RNase HII, and 2.0 Å for the 47 Cα atoms consisting of the core β-sheet of Ec-RNase HI. Active-site residues are shown by white stick models. The "basic protrusion" of Ec-RNase HI is indicated by a yellow arrow. (C) A close-up view of the active-site of the three RNases H. The view direction is the same as in the panel B and in Figure 1 ▶.
