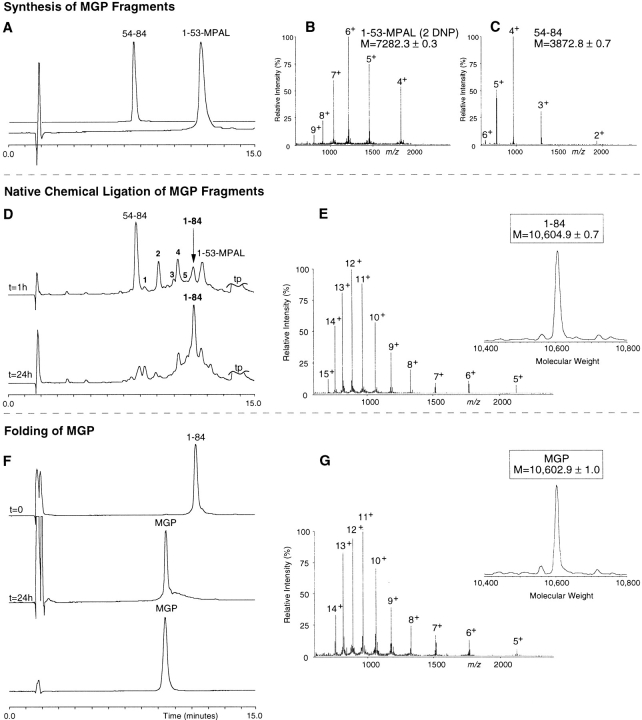
Fig. 3.
Total synthesis of human matrix Gla protein by native chemical ligation. Synthesis of MGP fragments: (A) HPLC chromatogram (C18: 22.5%–41% acetonitrile, 1.23%/min) of the starting synthetic peptide segments MGP 54–84 and MGP 1–53. (B) ESI-MS spectrum of MGP 1–53 shows the m/z ratios (fourth through ninth ionized states) with an calculated mass of 7282.3 ± 0.3 D (theoretical average mass of 7282.6). (C) ESI-MS spectrum of MGP 54–84 shows the m/z ratios (second through sixth ionized states) with an calculated mass of 3872.8 ± 0.7 D (theoretical average mass: 3873.4 D). Native chemical ligation of MGP fragments: (D) HPLC chromatograms of the ligation reaction, started by the addition of 2% (v/v) thiophenol and 2% benzylmercaptan to the peptide mixture MGP 1–53 and MGP 54–84. At t = 1 h, ligated product (1–84) is shown as well as the C-terminal segment starting material. The unreacted N-terminal material can be accounted for as multiple intermediates eluting between 7 and 13 min (see text). At t = 24 h, ligation was almost complete. (E) ESI-MS spectrum shows the m/z pattern of the ligated material (fifth through fifteenth ionized states) with a calculated mass of 10,604.9 ± 0.7 D (theoretical average mass of the reduced 84-residue MGP: 10,604.8 D). Folding and disulfide formation of MGP: (F) HPLC chromatograms of the purified, reduced MGP polypeptide (t = 0), the crude, folded material (t = 24 h), and the purified final product (MGP). (G) ESI-MS spectrum shows the m/z pattern (fifth through fourteenth ionized state) with a calculated molecular mass of 10,602.9 ± 1.0 D (theoretical average mass of MGP containing one disulfide: 10,602.8 D).