Fig. 5.
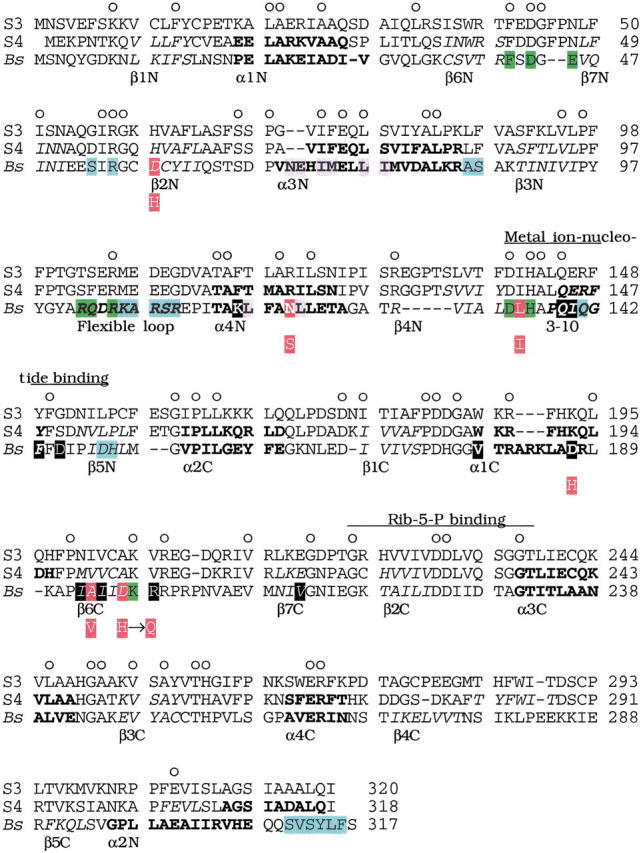
Alignment of amino acid sequences of spinach PRPP synthase isozyme 3 and 4 with B. subtilis PRPP synthase. Abbreviations: S3, spinach PRPP synthase isozyme 3; S4, spinach PRPP synthase isozyme 4 (Krath and Hove-Jensen 1999); Bs, B. subtilis PRPP synthase (Nilsson et al. 1989). Numbers (right) indicate amino acid position. Circles above the spinach PRPP synthase isozyme 3 sequence indicate positions with identical amino acids in the three sequences. Elements of secondary structure of B. subtilis PRPP synthase are indicated by amino acids in italics (β-sheet), bold (α-helix), or italics and bold (a 3–10 helix and a flexible loop) (Eriksen et al. 2000). The designation of each structural element is given below the B. subtilis PRPP synthase amino acid sequence. Similarly, predicted secondary structural elements of spinach PRPP synthase isozyme 4 are indicated in italics and bold as for the B. subtilis sequence. Green shading indicates amino acid residues of the active site of B. subtilis PRPP synthase. These residues were ideied by analysis of the crystal structure obtained as α,β-methylene ADP in complex with the enzyme, by analysis of the E. coli prs-1 specified mutant PRPP synthase altered in Asp129 (homologous with Asp134 of the B. subtilis sequence; Bower et al. 1989), or by analysis of affinity labeling of S. enterica PRPP synthase His131 (homologous with His136 of the B. subtilis sequence; Harlow and Switzer 1990), or of E. coli PRPP synthase Lys194 (homologous with Lys198 of the B. subtilis enzyme; Hilden et al. 1995). Blue shading indicates amino acid residues of the allosteric site of B. subtilis PRPP synthase ideied by analysis of the binding of α,β-methylene ADP in the crystal structure (Eriksen et al. 2000). The amino acid sequence ms ideied previously and designated by divalent metal ion-nucleotide binding (Bower et al. 1989) and by Rib-5-P binding (Hove-Jensen et al. 1986; Willemoës et al. 1996) are indicated by lines above the spinach PRPP synthase isozyme 3 amino acid sequence. Grey shading indicates amino acid residues ideied as involved in the formation of the so-called bent dimer of B. subtilis PRPP synthase. Black shading (white letters) indicates amino acid residues ideied as involved in the formation of the so-called parallel dimer of B. subtilis PRPP synthase (Eriksen et al. 2000). Red shading (white letters) of the B. subtilis PRPP synthase sequence indicates amino acids homologous with amino acids altered in the human PRPP synthase 1 owing to point mutations in the PRSP1 gene. Asp187, which belongs to this group of amino acids, is shaded in black. The amino acid of the mutant variant of human PRPP synthase 1 is shown below the B. subtilis sequence as a white letter with red shading. The actual alterations of human PRPP synthase 1, with the position of the homologous amino acid of B. subtilis PRPP synthase shown in parentheses, were: Asp51 → His (Asp58), Asn113 → Ser (Asn120), Leu128 → Ile (Leu135), Asp182 → His (Asp187), Ala189 → Val (Ala194). In addition, the alteration His192 → Gln was found in human PRPP synthase 1 (Becker et al. 1995). B. subtilis has aspartate at this position.
