Fig. 1.
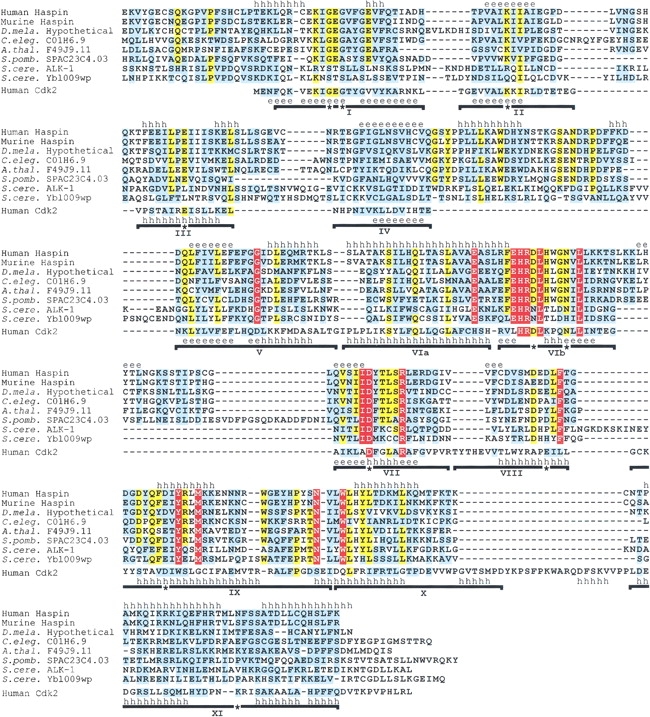
Multiple sequence alignment of Haspin kinase domains and human Cdk2. Residues that are completely conserved in all Haspin-like proteins are shown in white on a red background. Residues that are identical (yellow background) or similar (cyan background, based on Gonnet Pam250 matrix positive values) in ≥80% sequences are indicated. Introduced gaps are shown as dashes. Subdomains I to XI of the Cdk2 kinase fold are indicated with horizontal lines, and residues that are essentially invariant in previously identified kinases are labeled with asterisks (Hanks and Quinn 1991). The known secondary structure of Cdk2 is shown above its sequence (PDB code 1FIN). Above the alignment is a secondary structure prediction using PHDsec (Rost and Sander 1993), based on the alignment without Cdk2. Regions predicted with an expected accuracy of >82% to form α-helices (h) or β-strands (e) are labeled. The alignment includes residues 461–798 of human Haspin (GenBank AF289865); 417–754 of murine Haspin (GenBank AF289866, NP_034483); and the C-terminal regions of hypothetical proteins from D. melanogaster (see Materials and Methods), C. elegans (residues 564–920 of hypothetical protein C01H6.9, GenBank CAA95786), A. thaliana (residues 263–599 of hypothetical protein F14J9.11, GenBank AAC33205), S. pombe (residues 134–488 of hypothetical protein SPAC23C4.03, GenBank CAB16874), and S. cerevisiae (residues 408–759 of ALK-1/Ygl021w, GenBank P43633, CAA61012; and 324–676 of hypothetical protein Ybl009wp, GenBank NP_009544); and the entire sequence of human Cdk2 (residues 1–298, GenBank NP_001789). The PSI-BLAST E values after a single iteration when searching with human Haspin residues 461–798 were murine Haspin, 10−164; C01H6.9, 10 −103; F49J9.11, 10 −108; SPAC23C4.03, 7 × 10−97; ALK-1, 3 × 10−19; and Ybl009wp, 6 × 10−44.
