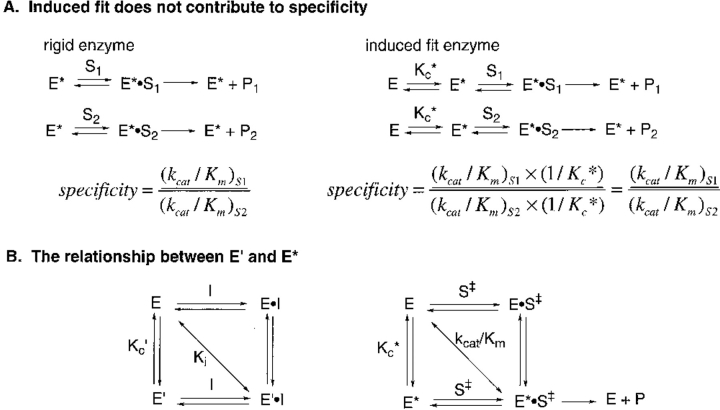
Fig. 1.
Schemes describing induced fit and conformational equilibrium. (A) Induced fit does not contribute to enzyme catalysis (Fersht 1985). E* denotes the active enzyme conformation; E, the inactive conformation; Kc*, the equilibrium constant for the interconversion of E and E*; S1 and S2, the two different substrates; and P1 and P2, their respective products. (B) The relationship between E′ and E*. I denotes the inhibitor; E′ indicates the enzyme conformation that binds inhibitor; Kc′, the equilibrium constant for the interconversion of E and E′; and S‡, the transition state structure of substrate S which is converted to product P. The experimental value of Ki measures the overall dissociation reaction of E′ • I to E and I as denoted by the diagonal. Similarly, the value of kcat/Km measured the transformation of E and S to E* • S‡. If E′ and E* are similar, then Kc′ and Kc*. should be related and a correlation will be observed between Ki and kcat/Km.