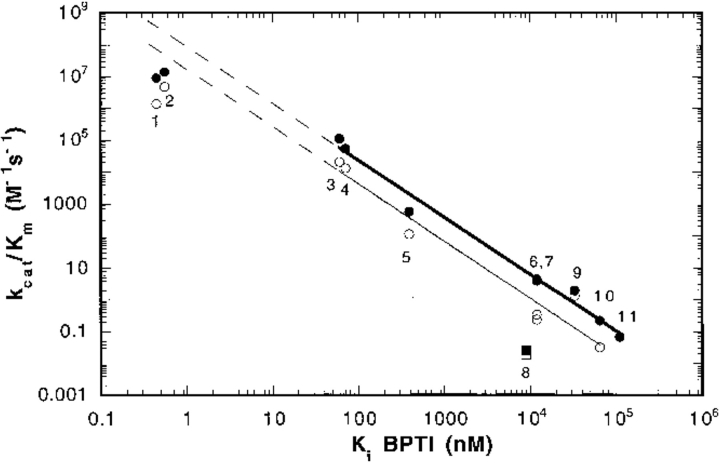
Fig. 4.
The correlation between BPTI affinity and kcat/Km for mutant rat trypsin(ogens). The values of the Ki of BPTI inhibition and kcat/Km for the hydrolysis of Tos-Gly-Pro-Arg-AMC (closed circles and square) and Tos-Gly-Pro-Lys-AMC (open circles and square) of the following rat trypsin(ogen) II mutants: wild-type (1), I16V trypsin (2), I16A trypsin (3), D194N trypsin (4), I16G trypsin (5), K15A trypsinogen (6), ΔI16V17/D194N trypsinogen (7), ΔI16V17 trypsinogen (8), ΔI trypsin (9), ΔI16V17/Q156K trypsinogen (10), and I16G trypsinogen (11). The data for ΔI16V17 trypsinogen (squares) were omitted from the correlation. Data for wild-type trypsin, D194N trypsin, I16V trypsin, I16A trypsin, and I16G trypsin were reported in Hedstrom et al. (1996); data for K15A trypsinogen, I16 trypsinogen, ΔI16V17/D194N trypsinogen, ΔI16 trypsin in Pasternak, et al. (1998); data for ΔI16V17/Q156K trypsinogen in this study; and data for ΔI16V17 trypsinogen in Pasternak, et al. (1998). No Tos-Gly-Pro-Lys-AMC data is available for I16G trypsinogen. The dashed lines show the extrapolation of the correlation to wild-type trypsin.