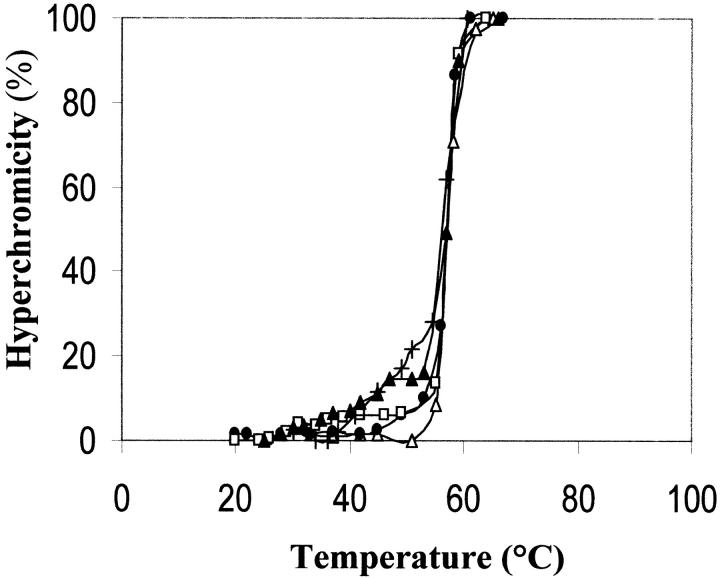
Fig. 3.
Effect of monomeric RNase A and its aggregates on the thermal transition profile of poly(dA-dT) • poly(dA-dT). 1.4 mL of 0.01 M imidazole-HCl/0.035 M NaCl buffer, pH 7, contained (in a stoppered cuvette) double-stranded poly(dA-dT) • poly(dA-dT) (13 μg/mL), and the various RNase A species (14 μg/mL). Absorbances at 260 nm were determined with a Beckman DU 650 spectrophotometer, equipped with a thermostatically controlled water bath, after maintaining the nucleic acid–protein mixture at the chosen temperature for 2.5 min (i.e., after hyperchromicity reached a stable value). (Open triangle) thermal transition profile of the nucleic acid in the absence of protein(s). (Filled circle) RNase A monomer; (open square) its major dimer (D2); (filled triangle) its more basic trimer (T2); (+) its more basic tetramer (TT2). Starting value of A260 was about 0.250. The contribution of protein(s) was nil.