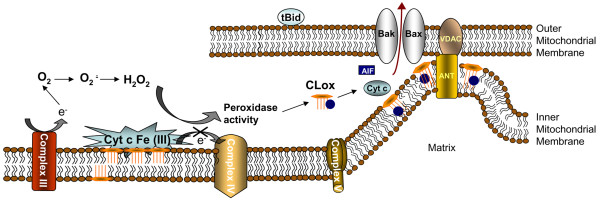
Figure 4.
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production and oxidative signaling in apoptosis. Interactions of cytochrome c (Cyt c) with the mitochondria specific phospholipid cardiolipin (CL) result in a high affinity cytochrome c-CL complex that acts as a specific and potent oxidant. In the presence of hydrogen peroxide, this complex functions as a CL-specific oxygenase catalyzing oxidation of CL. Binding with CL turns off cytochrome c's function as an electron carrier but turns on its peroxidase activity. Oxidized CL has a markedly lower affinity for cytochrome c and abandons the complex. CL oxidation products (CLox; mostly cardiolipin hydroperoxides) accumulate in the mitochondria, leading to the release of pro-apoptotic factors into the cytosol (Figure 4). AIF, apoptosis inducing factor; ANT, adenine nucleotide translocase; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion-selective channel.