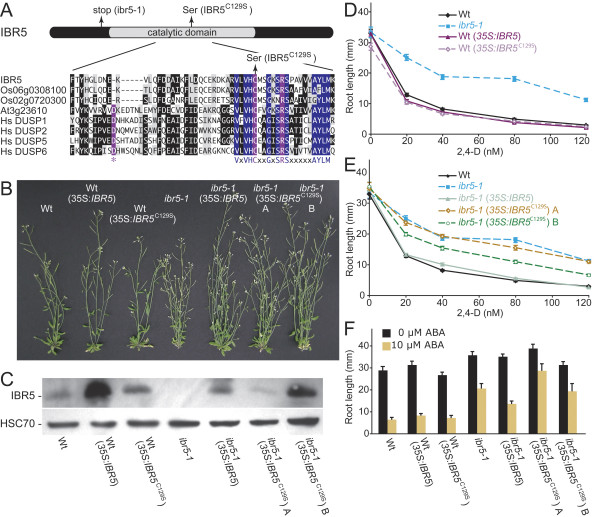
Figure 8.
An IBR5C129S substitution variant does not fully rescue ibr5 defects. (A) A schematic showing the positions of the ibr5-1 premature stop codon relative to the conserved catalytic domain and an alignment of part of the phosphatase catalytic domains of Arabidopsis IBR5 and several putative and confirmed DSP proteins. Sequences shown are the closest IBR5 homologs from rice (Os06g0308100 and Os02g0720300), an IBR5 relative from Arabidopsis with demonstrated DSP activity (At3g23610/DsPTP1; [52]) and three human (Hs) DSP enzymes. Sequences were aligned with the MegAlign program (DNAStar, Madison, WI) using the CLUSTAL W method. Catalytic residues are shaded in purple, conserved DSP signature residues are shaded in blue, residues identical in at least four sequences are shaded in black, similar residues are shaded in gray, and dashes indicate gaps introduced to maximize alignment. (B) Six-week-old Col-0 (Wt), Wt (35S:IBR5), Wt (35S:IBR5C129S), ibr5-1, ibr5-1 (35S:IBR5), ibr5-1 (35S:IBR5C129S) line A, and ibr5-1 (35S:IBR5C129S) line B grown in continuous light are shown. (C) Immunoblot analysis with an anti-IBR5 antibody [37]; top panel) and anti-HSC70 antibody (Stressgen Bioreagents) of protein prepared from 2-day-old seedlings of the lines shown in panel B. Positions of IBR5 and HSC70 are indicated at left. (D) Wt (35S:IBR5) and Wt (35S:IBR5C129S) display similar 2,4-D response as Wt. Lengths of primary roots of 8-day-old seedlings grown under yellow-filtered light at 22°C on medium supplemented with various concentrations of 2,4-D are shown. Error bars represent standard errors of the means (n ≥ 18). (E) ibr5-1 (35S:IBR5C129S) line A, and ibr5-1 (35S:IBR5C129S) line B fail to fully rescue ibr5-1 2,4-D resistance. Seedlings were measured as in (D). Error bars represent standard errors of the means (n ≥ 17). (F) Length of primary roots 4 days after transfer of 4-day-old seedlings to either 0 (ethanol control) or 10 μM ABA medium. Error bars represent standard errors of the means (n ≥ 8).