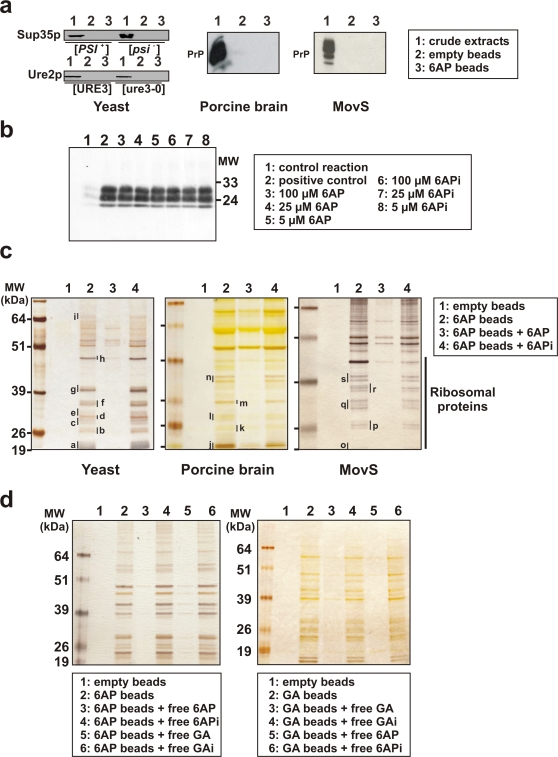
Figure 2. 6AP and GA do not interact with prion proteins but show specific interactions with ribosomal components and compete with each other for interaction with ribosomal components.
a. Extracts from yeast (left panel), porcine brain (middle panel) and murine MovS6 cells (right panel) were incubated with 6AP beads. The beads were then washed extensively and the bound proteins analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blotting analysis using antibodies directed against Sup35p, Ure2p or PrP as indicated. 1: crude extracts, 2: control beads without 6AP, 3: chromatography using 6AP beads. Note that none of the three prion proteins binds to 6AP beads. b. Protein Misfolding Cyclic Amplification (PMCA) reactions performed in the presence of various compounds and then subjected to proteinase K digestion followed by Western blot analysis using an anti-PrP antibody. All samples contain a mixture of normal and scrapie brain homogenates in addition to the tested compounds at various concentrations as indicated in the right panel. Note that both 6AP and 6APi are unable to inhibit in vitro conversion of PrPC to PrPSc. c. Extracts from yeast (left panel), porcine brain (middle panel) and murine MovS6 cells (right panel) were incubated with 6AP beads. The beads were then washed extensively and the bound proteins analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Lane 1: control beads without 6AP, lane 2: chromatography using 6AP beads, lane 3: competition with free 6AP, lane 4: competition with free 6APi, the inactive derivative of 6AP (see Figure 1a). Gels were silver-stained and specific bands were excised and analyzed by mass spectrometry. Note that for all the tested extracts, most of specific bands correspond to ribosomal proteins (see also table S1). d. Crude yeast cell extracts were incubated with 6AP beads (left gel) or GA beads (right gel). Lane 1: control beads without 6AP or GA, lane 2: chromatography using 6AP or GA beads, lanes 3 and 5: competition with free 6AP or GA, lanes 4 and 6: competition with free 6APi or GAi. The bound proteins were analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by silver-staining. Note that both 6AP and GA (but not 6APi and GAi) are able to compete for the binding of ribosomal components to both 6AP and GA beads, suggesting that they share common binding site(s).