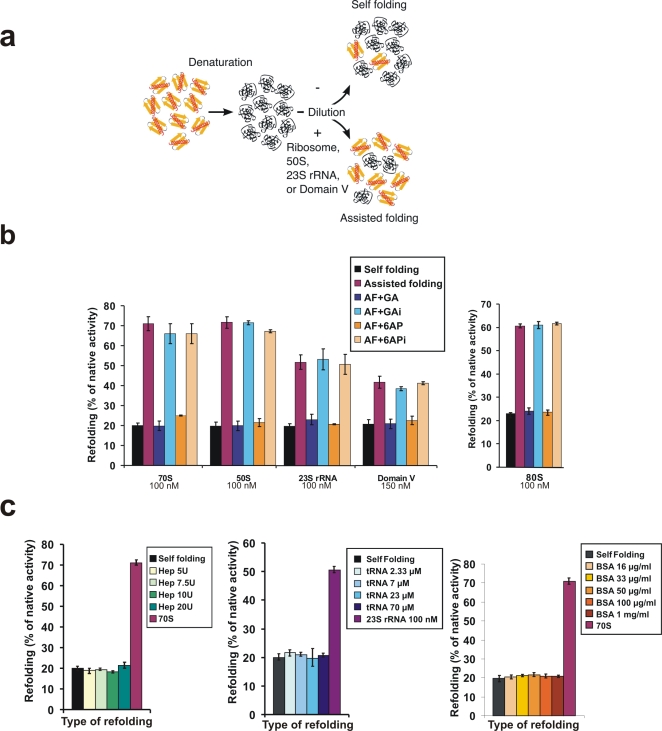
Figure 5. 6AP and GA specifically inhibit the protein folding activity of the ribosome in vitro.
a. Scheme depicting the principle of the in vitro assay to evaluate the protein folding activity of the ribosome. Human Carbonic Anhydrase (hCA) was denaturated (using GuHCl and EDTA) and then diluted into native buffer to allow refolding. Correct refolding was assessed by measuring the recovery of enzymatic activity as a function of time. Spontaneously, about 20% of the enzyme is able to refold correctly (Self folding, upper part of the scheme). If either a preparation of ribosomes, or the large subunit (50S), or the 23S rRNA, or the domain V of 23S rRNA, are added, the fraction of enzyme able to refold correctly increases up to 70%, due to the protein folding activity of the domain V of 23S rRNA of the large subunit of the ribosome (Assisted Folding -AF-, lower part of the scheme). b. Effect of the various drugs (as indicated) on assisted folding of hCA by eukaryotic (yeast S. cerevisiae, right panel) or prokaryotic (E. coli left panel) ribosomes (or indicated part of it). Concentration of each folding modulator is indicated. Note that only GA and 6AP, but not GAi and 6APi, were able to inhibit the assisted folding down to the level of self folding. c. Effect of heparin (left panel), tRNA (central panel) or BSA (right panel) on assisted folding of hCA. Note that none of these molecules is able to assist folding of hCA. Negative control is self folding and positive control is the assisted folding by 70S ribosome (for heparin and BSA experiments) or by 23S rRNA (for tRNA experiment).