Figure 1.
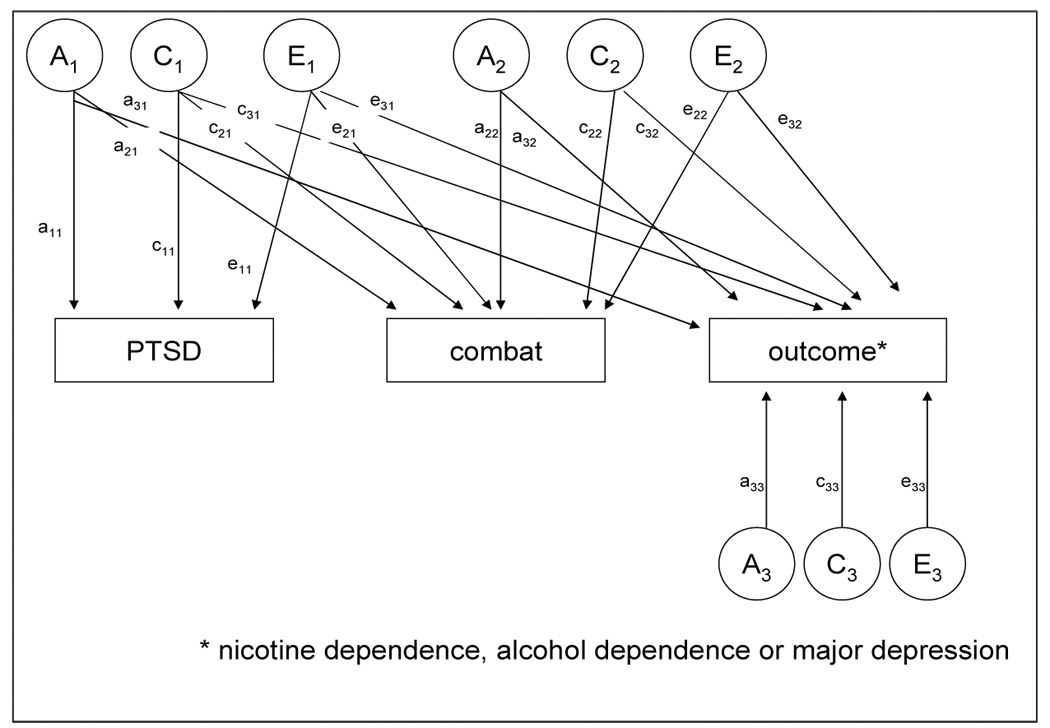
Full Cholesky model of additive genetic (A), family environmental (C) and unique environmental (E) contributions to posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), combat exposure and outcome phenotypes: nicotine dependence, alcohol dependence and major depression.
