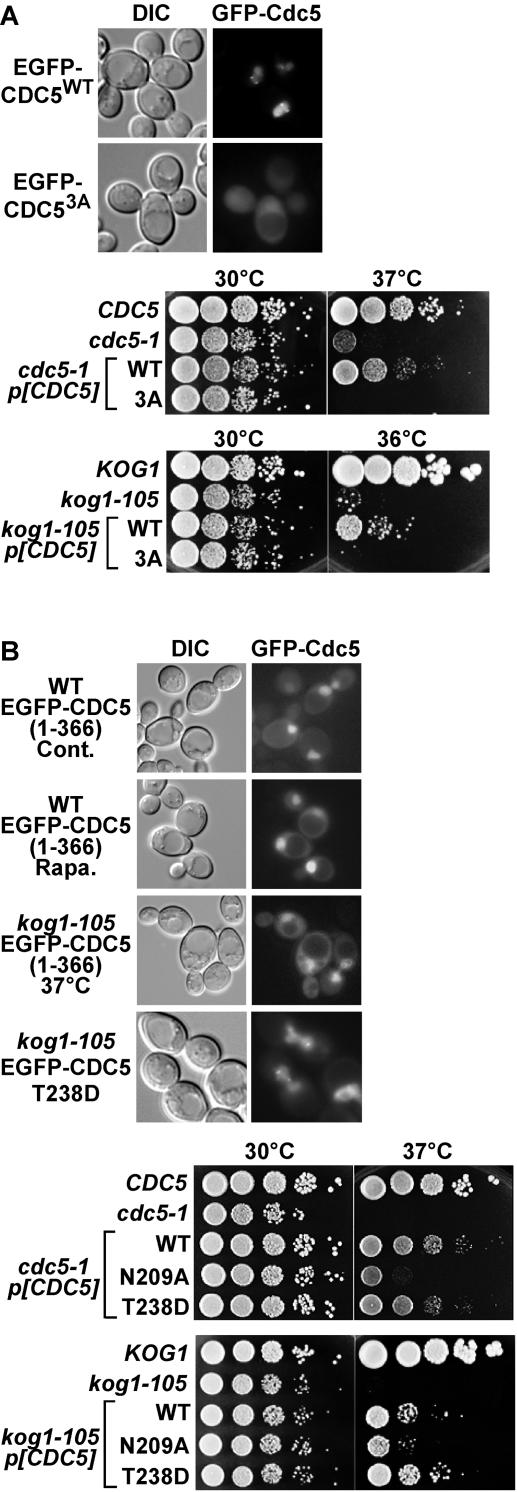
Figure 5. The C-terminus of Cdc5 has an inhibitory role in its nuclear translocation.
(A) (Top) Cells (W303-1B) expressing EGFP-Cdc5 (wild-type or NLS mutant (3A)) grown in SCD at 30°C were observed by fluorescent microscope. (Bottom) Wild-type (CDC5, KLY1548), cdc5-1 (KLY2156), and cdc5-1 cells harboring the indicated high-copy EGFP-CDC5 plasmids were spotted onto YEPD plates and incubated at 30 or 37°C for 2 days. Wild-type (YYK409), kog1-105 (YYK410), and kog1-105 cells harboring the indicated EGFP-CDC5 plasmids were spotted onto YEPD. (B) (Top) Cells (KOG1 and kog1-105) expressing EGFP-tagged N-terminus of Cdc5 (Cdc5(1-366)) or T238D mutant (full length) grown in SCD at 30°C were treated with 200 ng/ml rapamycin or incubated at 37°C for 2 h. (Bottom) Experiment shown in the bottom panel of Figure 5A was carried out using the indicated high-copy EGFP-CDC5 plasmids.