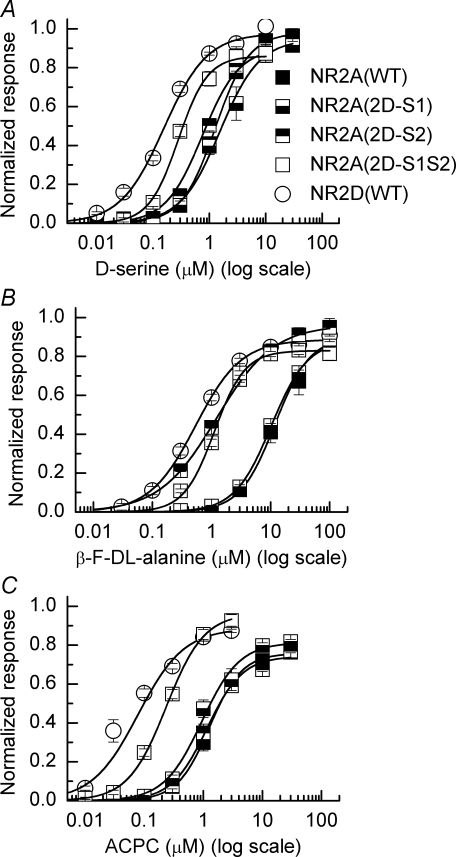
Figure 5. Concentration–response curves for d-serine,β-fluoro-dl-alanine and ACPC acting at wild-type and chimeric NMDARs.
A, mean concentration–response curves for d-serine acting at NR1/NR2A(WT) and NR1/NR2D(WT) NMDARs as well as each of the three chimeric NMDARs. B, mean concentration–response curves for β-fluoro-dl-alanine. C, mean concentration–response curves for ACPC. For each agonist, replacing the S1 and S2 region of the NR2A subunit with the corresponding regions from the NR2D subunit resulted in an increase in agonist potency. Mean EC50, Hill slope and ‘relative efficacy’ values for each of the agonists acting at the various NMDAR combinations are given in Fig. 6.