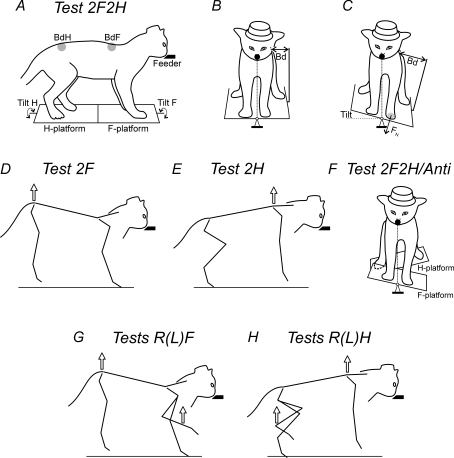
Figure 1. Postural tests.
The cat was standing on two platforms, one under the forelimbs (F-platform) and one under the hindlimbs (H-platform). The platforms were tilted in the frontal (roll) plane. The cat was continuously licking food from a feeder (feeder position is indicated by the filled bars in the side views and by the filled circles in the front views). A–C, in-phase tilts of the two platforms. A, the body outline (view from the right side) is shown for the horizontal position of the platforms. B and C, the body outline (view from the front) is shown for two positions of the platforms, horizontal and 15 degrees L, respectively. Postural corrections were characterized by measuring the lateral displacement of the upper point of the fore and hind parts of the trunk in relation to the corresponding platform (body displacements, BdF and BdH, in A–C). The normal component of the contact force produced by each limb was measured by means of a force plate (shown for only the left forelimb, FN in C). D, lifting the hindquarters. E, lifting the forequarters. F, antiphase tilt of the two platforms. G, lifting the hindquarters and one forelimb. H, lifting the forequarters and one hindlimb.