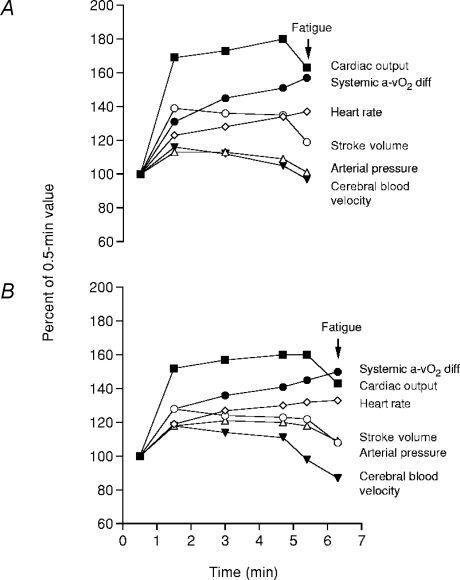
Figure 5. Effects of heat stress (A) on systemic haemodynamics and cerebral circulation during maximal exercise compared to control (B) conditions.
Time to fatigue while cycling at 360 ± 10 W was diminished in heat stress compared to control (5.8 ± 0.2 versus 7.5 ± 0.4 min, respectively). Note that fatigue in both conditions was preceded by reductions in cardiac output, stroke volume, arterial blood pressure and middle cerebral arterial blood velocity. Redrawn from González-Alonso et al. (2004).