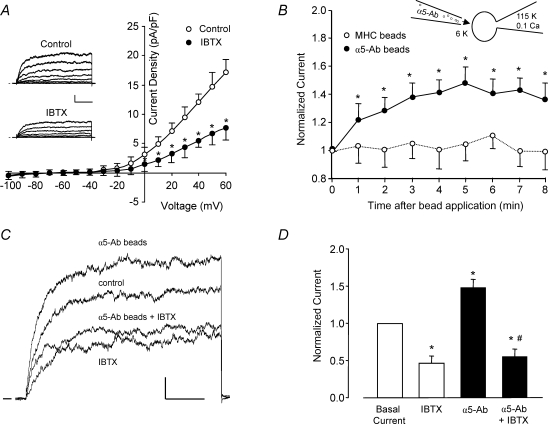
Figure 1. An outward, IBTX-sensitive K+ current is enhanced by α5β1 integrin activation.
A, average outward current (expressed as current density, pA pF−1) from freshly isolated rat cremaster muscle arteriolar myocytes is plotted as a function of voltage (test pulse), with or without 100 nm IBTX present in the bath (n = 6). Inset, representative whole-cell current traces from a single myocyte under control conditions and with 100 nm IBTX in the bath. Calibration bar: 100 pA, 50 ms. Vh=−60 mV. B, time course of K+ current enhancement following α5β1 integrin activation by beads coated with anti-rat α5 integrin antibody (HMα5-1); beads were applied from a picospritzer pipette (∼5 beads cell−1). Beads coated with anti-rat MHC Class I Ab were used as a control to test for a mechanical artifact (○, n = 7). Inset shows the recording configuration for panels B–D, with the bath solution containing 6 mm K+ and pipette solution containing 115 mm K+ and 0.1 μm Ca2+. C, sample recordings of whole-cell K+ current from two arteriolar myocytes in the absence and presence of α5β1 integrin activation and IBTX (100 nm). Holding potential =−60 mV, test potential =+50 mV, duration = 200 ms. α5β1 integrin was activated by α5β1 integrin Ab bound to beads (3 beads for this cell). In a second cell, the potentiation of current in response to integrin activation was blocked in the presence of IBTX (100 nm). Calibration bar: 100 pA, 50 ms. D, summary of effects of insoluble α5-Ab on BK current in VSM in the absence (n = 5) or presence of IBTX (n = 6). Bath solution, 136 Na++ 4-AP (1 mm) + glibenclamide (500 nm); pipette, 115 K+ (0.1 μm[Ca2+]). *P < 0.05 versus control (basal current); #P < 0.05 versusα5-integrin Ab.