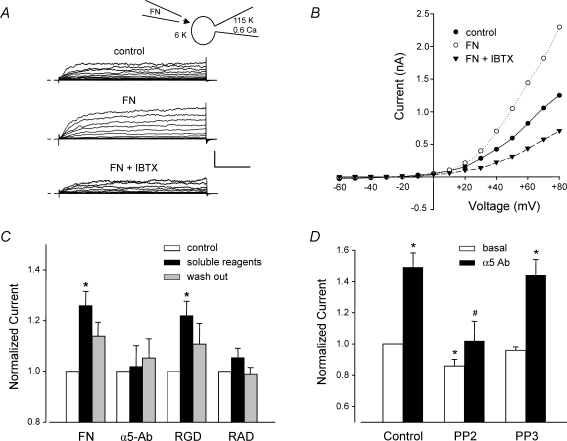
Figure 2. Effects of different α5β1 integrin ligands on whole-cell VSM K+ current.
A, representative recordings of whole-cell K+ currents before (control), 3 min after application of soluble FN (10 μg ml−1), and after subsequent addition of IBTX (100 nm) to the bath. Calibration bar: 500 pA, 50 ms. Inset shows recording configuration for all panels. Vh=−70 mV. B, I–V curves derived from current tracings shown in panel A. C, summary of peak K+ currents in response to a +50 mV voltage step in which the cells were treated with the following agents for 4 min: soluble FN fragment (10 μg ml−1), soluble RGD peptide (100 μm), soluble α5 integrin Ab (15 μg ml−1), or soluble RAD (control peptide for RGD, 100 μm). *P < 0.05 versus control. D, the soluble c-Src inhibitor PP2 (100 nm, n = 8) significantly blocked the potentiation of K+ current by insoluble α5-integrin Ab (measured at 5 min). Pretreatment of cells with PP2 (100 nm) significantly inhibited basal current and prevented enhancement of current after α5β1 integrin activation. The inactive analogue PP3 (100 nm, n = 8) slightly but not significantly decreased basal BK current and did not significantly alter enhancement of current after α5β1 integrin activation. All values were normalized to the value of control current at a test potential of +50 mV; Vh=−60 mV. For panels A and B, the bath solution was 140 mm Na+, 6 mm K++ 4-AP (1 mm) + glibenclamide (500 nm); the pipette solution contained 115 mm K+ and 0.6 μm Ca2+. For panels C and D the bath solution was 136 Na++ 1 mm 4-AP + 500 nm glibenclamide; pipette solution: 115 K+ with 100 nm Ca2+. *P < 0.05 versus control (basal current). #P < 0.05 versus control α5-Ab.