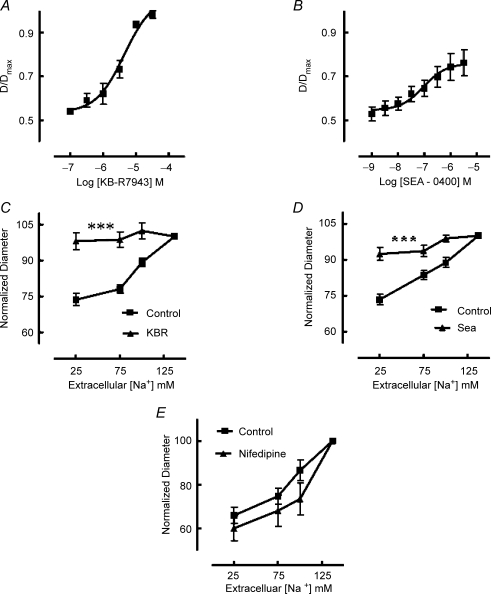
Figure 2. Effect of NCX inhibitors KB-R7943 and SEA 0400 on arteriolar diameter (A and B) and responses to extracellular Na+ reduction (C and D).
KB-R7943 (A; n = 9) and SEA 0400 (B; n = 9) caused concentration-dependent vasodilatation with the former causing near maximal relaxation. Both inhibitors blocked the vasoconstrictor response to reduced extracellular Na+ concentrations (C and D) consistent with an effect on reverse mode (Ca2+ influx) NCX activity. Data in C (n = 9) and D (n = 9) have been normalized such that D/Dmax at an extracellular Na+ concentration of 137 mm is represented as 100%. As the NCX inhibitors caused vasodilatation control studies were performed with nifedipine (10−6m). Nifedipine, while causing vasodilatation, did not inhibit subsequent constriction in response to extracellular Na+ reduction (E; n = 4). Results are expressed as means ± s.e.m.; ***P < 0.001.