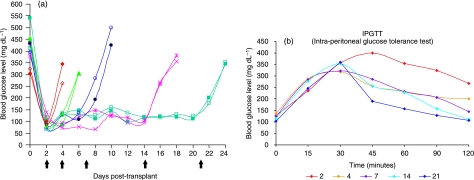
Fig. 1.
In vivo functionality of transplanted pancreatic islets. (a) Blood glucose level determined before the injection of streptozotocin (STZ), just before the transplant (day 0) and in the post-transplant follow-up. Note the induction of diabetes, the stable normalization of glycaemia approximately 3 days after the transplant, and the re-induction of diabetes after the nephrectomy (⇑). (b) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance tests (IPGTTs) performed on six animals for each time point (see also Table 2). After the intraperitoneal injection of glucose, blood glucose levels were measured at 15, 30, 45, 60, 90 and 120 min. An abnormal response was observed in the immediate post-transplant period (2 and 4 days). Animals at 21 days after the transplant showed the best response with lower levels of glycaemia at 45 min post-glucose infusion and normal levels after 120 min, while at 7 and 14 days an intermediate response to the test was observed.