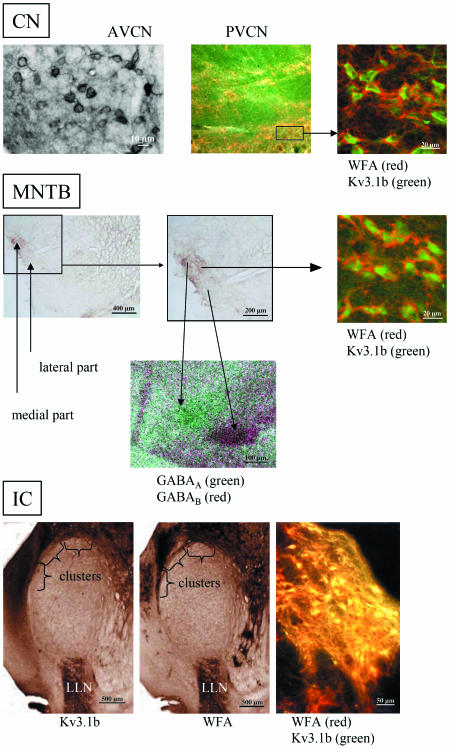
Fig. 1.
Comparison of the distribution patterns of perineuronal nets as revealed by WFA binding sites and Kv3.1b protein in the relay stations of the auditory brainstem of the rhesus monkey. The distribution patterns change from non-compartmentalization in the anterior ventral cochlear nucleus (AVCN) with intermingled intensely and weakly stained WFA to clusters (see window) in the posterior ventral cochlear nucleus (PVCN), via subnucleation into a medial part with intensely stained WFA and a lateral part of the MNTB (additionally revealed by GABAA and GABAB receptors) to clusters in the external nucleus of the inferior colliculus (IC); LLN, lateral lemniscal nucleus. The heavily stained WFA binding was revealed by confocal laser scanning microscopy as thick, red perineuronal nets and is co-localized with green labelled Kv3.1b protein at the soma of the auditory neuron. In the overview, yellow colour indicates co-localization of Kv3.1b with dark WFA binding sites in a cluster.