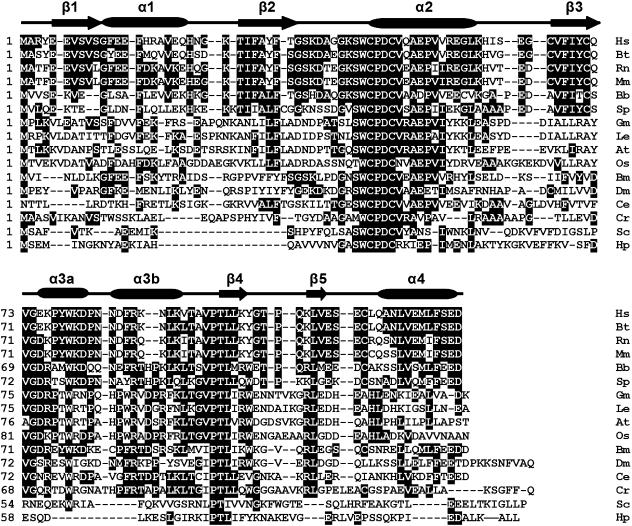
Fig. 1.
Alignment of the amino acid sequences of AmphiTRP14 with other TRP14 proteins including human TRP14 and putative TRP14 proteins using the MegAlign program (DNASTAR) by the CLUSTAL W method. Shaded (with solid black) residues are the amino acids that match the consensus. Gaps introduced into sequences to optimize alignment are represented by a dash. The secondary structures of human TRP14 protein (PDB: 1WOU) are marked at the peak of the corresponding sequences. β-strands are shown as arrows and α-helices are shown as cylinder. The conserved active motif is marked by closed inverted triangles. The sequences used are: Hs (Homo sapiens, BC006405), Bt (Bos taurus, AW917424), Rn (Rattus norvegicus, AW917424), Mm (Mus musculus, NM_026559), Bb (Branchiostoma belcheri, EF065518), Sp (Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, XP_787642), Gm (Glycine max, AW734061), Le (Lycopersicon esculentum, AW223476), At (Arabidopsis thaliana, BAB09186), Os (Oryza sativa, BE040654), Bm (Bombyx mori, AU003992), Dm (Drosophila melanogaster, CAB58075), Sc (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, NP_013468), Ce (Caenorhabditis elegans, AV193251), Cr (Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, BE056551), Hp (Helicobacter pylori, B64702).