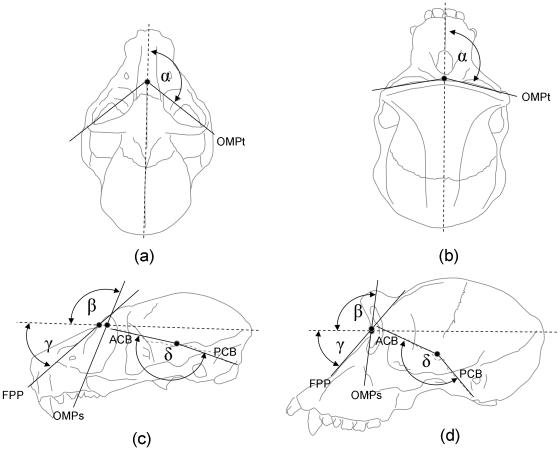
Fig. 1.
Diagrams of a lemur (Lemur catta; a,c) and a chimp (Pan troglodytes; b,d) skull in superior (a,b) and lateral (c,d) profile illustrating measurements of convergence, frontation, midfacial prognathism and orbito-facial integration: MSP, midsagittal plane (broken line, a,b); OMPt, plane that passes through the medial- and lateral-most margins of the orbit and intersects with MSP; the angle of orbital convergence is equal to 180° – α; INP, plane from inion to nasion (broken line, c,d); OMPs, plane that passes through the superior- and inferior-most margins of the orbit and intersects with INP; the angle of orbital frontation is equal to 180° – β; FPP, midfacial prognathism plane through nasion and the anterior nasal spine; the angle of facial projection is equal to 180° – γ; ACB and PCB, planes marking the endocranial surfaces of the anterior cranial base and posterior cranial base, respectively; the angle of cranial base flexion is equal to δ. Not to scale.