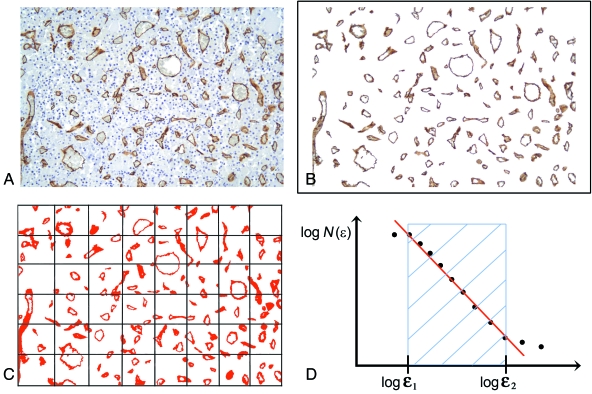
Fig. 2.
Computer-aided estimate of the surface area fractal dimension (D) of a vascular network in two-dimensional biopsy sections. (A) Pituitary tissue section stained with antibodies raised against CD34 that specifically react with vessels. (B) Image segmentation: the immunopositive vessels are selected on the basis of the similarity of the colour of adjacent pixels. (C) Determination of D using the box-counting algorithm which, briefly, counts the number of boxes of length ɛ required to cover the object being measured, and indicated as N(ɛ). (D) Prototypical curve obtainable using the box-counting method that highlights the so-called fractal windows ranged by box size ɛ1 and ɛ2, and represents the appropriate region in which to estimate the dimension. Box sizes of more than ɛ2 approach the size of the image until one box covers it completely. Box sizes smaller than ɛ1 approach a single pixel or the resolution of the image.